Example for Configuring LDP over TE
This section provides an example for configuring LDP over TE. The configuration procedure involves the establishment of a TE tunnel and a remote LDP peer.
Networking Requirements
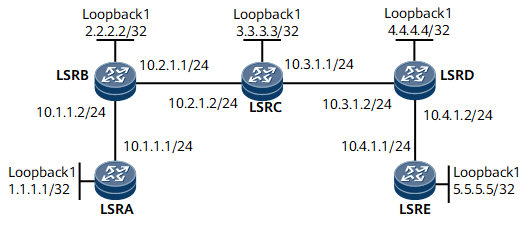
On the network shown in Figure 1, LSRB and LSRD are on the edge of a backbone network. LDP over TE is to be deployed on this network to allow an LDP LSP to across an RSVP-TE area. LDP services can be transmitted between LSRA and LSRB, and between LSRD and LSRE. In addition, TE services are transmitted between LSR B, LSRC, and between LSRC and LSRD. A TE tunnel destined for LSRD is established on LSRB, and an RSVP tunnel destined for LSRB is established on LSRD. Traffic between LSRA and LSRE needs to be transmitted through the tunnel. LDP over TE can transmit VPN services.
Device Name |
Interface Name |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
LSRA |
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
LSRB |
Loopback1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
LSRC |
Loopback1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
|
LSRD |
Loopback1 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
10.4.1.2/24 |
|
LSRE |
Loopback1 |
5.5.5.5/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.4.1.1/24 |
Configuration Notes
When configuring LDP over TE, note that the tunnel destination address must be the LSR ID of the egress.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address to each interface, configure the loopback address as the LSR ID, configure an IGP to advertise routes to the network segment connected to each interface and the host route to each LSR ID.
Enable OSPF TE in a TE-aware area and establish an MPLS TE tunnel.
Enable MPLS LDP in each non-TE-aware area and configure remote LDP peers at the edge of the TE-aware area.
Configure the forwarding adjacency.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
OSPF process ID and OSPF area ID
Policy for triggering the LSP establishment
Name and IP address of each remote LDP peer of LSRB and LSRD
Link bandwidth attributes of the tunnel
Tunnel interface number, IP address, destination address, tunnel ID, RSVP-TE tunnel signaling protocol, tunnel bandwidth, TE metric value, link cost on LSRB and LSRD
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface.
Assign an IP address to each interface in this section. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure OSPF to advertise the route to the network segment to which each interface is connected and the host route to each LSR ID. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable MPLS on each LSR. Enable LDP to set up LDP sessions between LSRA and LSRB, and between LSRD and LSRE. Enable RSVP TE to establish RSVP neighbor relationships between LSRB and LSRC, and between LSRC and LSRD.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*LSRA] mpls [*LSRA-mpls] quit [*LSRA] mpls ldp [*LSRA-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure LSRB.
[~LSRB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*LSRB] mpls [*LSRB-mpls] mpls te [*LSRB-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRB-mpls] mpls te cspf [*LSRB-mpls] quit [*LSRB] mpls ldp [*LSRB-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls te [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure LSRC.
[~LSRC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*LSRC] mpls [*LSRC-mpls] mpls te [*LSRC-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRC-mpls] quit [*LSRC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls te [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 [*LSRD] mpls [*LSRD-mpls] mpls te [*LSRD-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRD-mpls] mpls te cspf [*LSRD-mpls] quit [*LSRD] mpls ldp [*LSRD-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls rsvp-te [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure LSRE.
[~LSRE] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 [*LSRE] mpls [*LSRE-mpls] quit [*LSRE] mpls ldp [*LSRE-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~LSRE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
After the preceding configurations are complete, the local LDP sessions are successfully set up between LSRA and LSRB, and between LSRD and LSRE.
# Run the display mpls ldp session command on LSRA, LSRB, LSRD, or LSRE to view information about the established LDP session. The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
[~LSRA] display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) A '*' before a session means the session is being deleted. -------------------------------------------------------------------------- PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2.2.2.2:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:05 23/23 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOTAL: 1 Session(s) Found.# Run the display mpls ldp peer command on an LSR to view information about the established LDP peer. The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
[~LSRA] display mpls ldp peer LDP Peer Information in Public network An asterisk (*) before a peer means the peer is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------- PeerID TransportAddress DiscoverySource ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2.2.2.2:0 2.2.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOTAL: 1 Peer(s) Found.
# Run the display mpls lsp command on an LSR. You can view information about LDP LSPs and RSVP tunnels are not set up. The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
[~LSRA] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.1/32 3/NULL -/- 2.2.2.2/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/0 2.2.2.2/32 32841/3 -/GE0/1/0
- Configure a remote LDP session between LSRB and LSRD.
# Configure LSRB.
[~LSRB] mpls ldp remote-peer lsrd [*LSRB-mpls-ldp-remote-lsrd] remote-ip 4.4.4.4 [*LSRB-mpls-ldp-remote-lsrd] commit [~LSRB-mpls-ldp-remote-lsrd] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] mpls ldp remote-peer lsrb [*LSRD-mpls-ldp-remote-lsrb] remote-ip 2.2.2.2 [*LSRD-mpls-ldp-remote-lsrb] commit [~LSRD-mpls-ldp-remote-lsrb] quit
# After completing the preceding configurations, run the display mpls ldp remote-peer command on LSRB or LSRD. The commando output shows that a remote LDP session has been established between LSRB and LSRD. The following example uses the command output on LSRB.
[~LSRB] display mpls ldp remote-peer lsrd LDP Remote Entity Information ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Remote Peer Name : lsrd Description : ---- Remote Peer IP : 4.4.4.4 LDP ID : 2.2.2.2:0 Transport Address : 2.2.2.2 Entity Status : Active Configured Keepalive Hold Timer : 45 Sec Configured Keepalive Send Timer : ---- Configured Hello Hold Timer : 45 Sec Negotiated Hello Hold Timer : 45 Sec Configured Hello Send Timer : ---- Configured Delay Timer : 10 Sec Hello Packet sent/received : 425/382 Label Advertisement Mode : Downstream Unsolicited Auto-config : ---- Manual-config : effective Session-Protect effect : YES Session-Protect Duration : infinite Session-Protect Remain : ---- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 1 Remote-Peer(s) Found.
- Configure bandwidth attributes on each outbound interface along the link of the TE tunnel.
# Configure LSRB.
[~LSRB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [~LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure LSRC.
[~LSRC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure a tunnel from LSRB to LSRD.
# On LSRB, enable the forwarding adjacency on the tunnel interface and adjust the metric value of the forwarding adjacency to direct traffic destined for LSRD or LSRE to the tunnel.
[~LSRB] interface tunnel1 [*LSRB-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 [*LSRB-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*LSRB-Tunnel1] destination 4.4.4.4 [*LSRB-Tunnel1] mpls te tunnel-id 100 [*LSRB-Tunnel1] mpls te bandwidth ct0 10000 [*LSRB-Tunnel1] mpls te igp advertise [*LSRB-Tunnel1] mpls te igp metric absolute 1 [*LSRB-Tunnel1] quit [*LSRB] ospf 1 [*LSRB-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable [*LSRB-ospf-1] area 0 [*LSRB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls-te enable [*LSRB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*LSRB-ospf-1] enable traffic-adjustment advertise [*LSRB-ospf-1] commit
- Configure a tunnel from LSRD to LSRB.
# On LSRD, enable the forwarding adjacency on the tunnel interface and adjust the metric value of the forwarding adjacency to direct traffic destined for LSRA or LSRB to the tunnel.
[~LSRD] interface tunnel1 [*LSRD-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 [*LSRD-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*LSRD-Tunnel1] destination 2.2.2.2 [*LSRD-Tunnel1] mpls te tunnel-id 101 [*LSRD-Tunnel1] mpls te bandwidth ct0 10000 [*LSRD-Tunnel1] mpls te igp advertise [*LSRD-Tunnel1] mpls te igp metric absolute 1 [*LSRD-Tunnel1] quit [*LSRD] ospf 1 [*LSRD-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable [*LSRD-ospf-1] area 0 [*LSRD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls-te enable [*LSRD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*LSRD-ospf-1] enable traffic-adjustment advertise [*LSRD-ospf-1] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# After completing the preceding configurations, run the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on LSRB. The command output shows that the tunnels have been successfully established.
[~LSRB] display mpls te tunnel-interface Tunnel Name : Tunnel1 Signalled Tunnel Name: - Tunnel State Desc : CR-LSP is Up Tunnel Attributes : Active LSP : Primary LSP Traffic Switch : - Session ID : 100 Ingress LSR ID : 2.2.2.2 Egress LSR ID: 4.4.4.4 Admin State : UP Oper State : UP Signaling Protocol : RSVP FTid : 1 Tie-Breaking Policy : None Metric Type : None# Run the display ip routing-table command on LSRB to view route information. The command output shows that the outbound interfaces destined for LSRD and LSRE are tunnel interfaces.
[~LSRB] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 18 Routes : 19 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 2.2.2.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 3.3.3.3/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 4.4.4.4/32 OSPF 10 1 D 2.2.2.2 Tunnel1 5.5.5.5/32 OSPF 10 2 D 2.2.2.2 Tunnel1 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.2.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.3.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 2.2.2.2 Tunnel1 OSPF 10 2 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 2.2.2.2 Tunnel1 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
# Run the display mpls lsp command on LSRB, LSRC, or LSRD to view information about LSPs. You can view information about RSVP LSPs. The following example uses the command output on LSRB.
[~LSRB] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: RSVP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 4.4.4.4/32 NULL/32832 -/GE0/1/8 2.2.2.2/32 3/NULL GE0/1/8/- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.1/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/0 1.1.1.1/32 32834/3 -/GE0/1/0 2.2.2.2/32 3/NULL -/- 4.4.4.4/32 NULL/3 -/Tun1 4.4.4.4/32 32844/3 -/Tun1 5.5.5.5/32 NULL/32837 -/Tun1 5.5.5.5/32 32845/32837 -/Tun1
# Run the display ip routing-table command to view the routing table on LSRA. The command output shows that the cost values change after the forwarding adjacency was configured.
[~LSRA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 16 Routes : 16 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 2.2.2.2/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 3.3.3.3/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 4.4.4.4/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 5.5.5.5/32 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.0/24 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.4.1.0/24 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # returnLSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # mpls ldp remote-peer lsrd remote-ip 4.4.4.4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 mpls rsvp-te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 4.4.4.4 mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te bandwidth ct0 10000 mpls te igp advertise mpls te igp metric absolute 1 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable enable traffic-adjustment advertise area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 mpls rsvp-te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # mpls ldp remote-peer lsrb remote-ip 2.2.2.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 20000 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 2.2.2.2 mpls te tunnel-id 101 mpls te bandwidth ct0 10000 mpls te igp advertise mpls te igp metric absolute 1 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable enable traffic-adjustment advertise area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRE configuration file
# sysname LSRE # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 # mpls # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return