Example for Configuring Dynamic BFD to Monitor an LDP Tunnel
This section provides an example for configuring dynamic BFD to monitor an LDP tunnel. The configuration involves configuring LDP FRR and configuring dynamic BFD for LDP tunnel.
Networking Requirements
When LDP LSPs transmit application traffic, for example, VPN, to improve network reliability, LDP FRR and an LDP upper-layer protection mechanism, such as VPN FRR or VPN equal-cost multipath (ECMP), are used. BFD for LDP LSP only detects primary LSP faults and switches traffic to an FRR LSP. If the primary and FRR LSPs fail simultaneously, the BFD mechanism does not take effect. In this situation, LDP can instruct its upper-layer application to perform a protection switchover only after LDP detects the FRR LSP failure. As a result, a great number of packets are dropped.
To prevent packet loss occurring when BFD for LDP LSP cannot detect faults of the primary and backup LSPs, configure dynamic BFD for LDP tunnel to create a dynamic BFD session that monitors the primary LSP and FRR LSP. In this way, when both the primary LSP and FRR LSP are faulty, BFD can quickly detect and trigger the upper-layer application of the LDP to perform protection switching and reduce traffic loss.
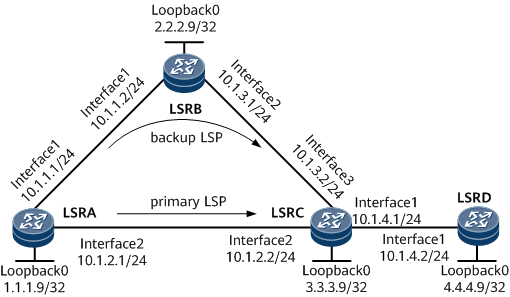
On the network shown in Figure 1, an LDP LSP originates from LSRA and is destined for LSRD. LDP Auto FRR is configured to protect LSP traffic. LSRA establishes the primary LSP over the path LSRA -> LSRC -> LSRD and the FRR LSP over the path LSRA -> LSRB -> LSRC -> LSRD. Dynamic BFD for LDP tunnel can be configured to dynamically create a BFD session to monitor both the primary and FRR LSPs.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Establish an LDP LSP between LSRA and LSRD.
Configure LDP Auto FRR on the ingress LSRA.
Configure a dynamic BFD session to monitor an LDP tunnel.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP address of each interface on each node: values shown in Figure 1.
LSR ID of each node: loopback addresses shown in Figure 1
IS-IS process number (1), IS-IS level (level-2), and network entity name of each node:
- LSRA: 10.0000.0000.0001.00
- LSRC: 10.0000.0000.0002.00
- LSRB: 10.0000.0000.0003.00
- LSRD: 10.0000.0000.0004.00
Name of a FEC list used to establish the BFD session: list1
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic IS-IS functions. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure LDP LSPs.
# Configure LSRA.
<LSRA> system-view [~LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*LSRA] mpls [*LSRA-mpls] quit [*LSRA] mpls ldp [*LSRA-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Repeat this step for LSRB, LSRC, and LSRD. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure LDP Auto FRR.
# Enable IS-IS Auto FRR on LSRA.
[~LSRA] isis 1 [*LSRA-isis-1] frr [*LSRA-isis-1-frr] loop-free-alternate level-2 [*LSRA-isis-1-frr] quit [*LSRA-isis-1] commit [~LSRA-isis-1] quit
After IS-IS Auto FRR is enabled, LDP Auto FRR automatically takes effect. Then, run the display mpls lsp command on LSRA to view information about the primary and FRR LSPs in the LDP tunnel.
[~LSRA] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.9/32 3/NULL -/- 2.2.2.9/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/1 2.2.2.9/32 32833/3 -/GE0/1/1 **LDP FRR** NULL/32835 -/GE0/1/0 **LDP FRR** 32833/32835 -/GE0/1/0 3.3.3.9/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/1 3.3.3.9/32 32837/3 -/GE0/1/1 **LDP FRR** NULL/32837 -/GE0/1/0 **LDP FRR** 32837/32837 -/GE0/1/0 4.4.4.9/32 NULL/32832 -/GE0/1/1 4.4.4.9/32 32836/32832 -/GE0/1/1 **LDP FRR** NULL/32836 -/GE0/1/0 **LDP FRR** 32836/32836 -/GE0/1/0 10.1.3.0/24 32834/3 -/GE0/1/0 10.1.3.0/24 32834/3 -/GE0/1/1 10.1.4.0/24 32835/3 -/GE0/1/1
- Enable BFD globally.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] bfd [*LSRA-bfd] commit [~LSRA-bfd] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] bfd [*LSRD-bfd] commit [~LSRD-bfd] quit
- Enable the ingress LSRA and egress LSRD to dynamically establish a BFD session.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] mpls [~LSRA-mpls] mpls bfd enable [*LSRA-mpls] commit [~LSRA-mpls] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] bfd [~LSRD-bfd] mpls-passive [*LSRD-bfd] commit [~LSRD-bfd] quit
- Configure a policy for triggering dynamic BFD for LDP tunnel.
# On LSRA, create a FEC list and add a node with IP address 4.4.4.4 to the list so that the FEC list is used to establish a BFD session only to monitor the LDP tunnel between LSRA and LSRD.
[~LSRA] fec-list list1 [*LSRA-fec-list-list1] fec-node 4.4.4.9 [*LSRA-fec-list-list1] commit [~LSRA-fec-list-list1] quit
# Specify the FEC list on LSRA so that LSRA uses it to establish a BFD session.
[~LSRA] mpls [~LSRA-mpls] mpls bfd-trigger-tunnel fec-list list1 [*LSRA-mpls] commit [~LSRA-mpls] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display mpls bfd session protocol ldp bfd-type ldp-tunnel verbose command on LSRA. The command output shows that a dynamic BFD session is Up.
[~LSRA] display mpls bfd session protocol ldp bfd-type ldp-tunnel verbose -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- BFD Information: LDP Tunnel -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- No : 1 LspIndex : 0 Protocol : LDP Fec : 4.4.4.9 Bfd-Discriminator : 16389 ActTx : 10 ActRx : 10 ActMulti : 3 Bfd-State : Up Time : 800 sec
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # bfd # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls mpls bfd enable mpls bfd-trigger-tunnel fec-list list1 # fec-list list1 fec-node 4.4.4.9 # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 frr loop-free-alternate level-1 loop-free-alternate level-2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return
LSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls lsp-trigger all # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls lsp-trigger all # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return
LSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # bfd mpls-passive # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 # mpls lsp-trigger all # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return