Configuring VPN ORF
After BGP peer relationships are established in the BGP-VPN-Target (VT) address family, VPN ORF filters the routes to be advertised to PEs based on the VPN target of each VPN instance bound to each PE.
Usage Scenario
As the network increases in size and complexity, a PE receives a larger number of routes. To enable the PE to receive only the expected routes, thereby reducing pressure on the PE, you can configure VPN ORF. After VPN ORF is enabled, the local device filters the routes to be advertised to PEs based on the VPN target of each VPN instance bound to each PE.
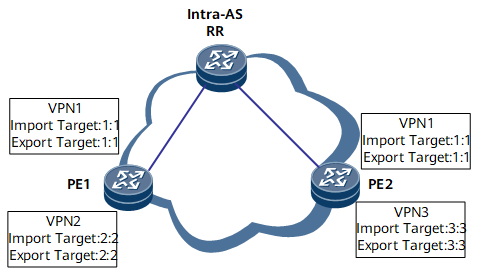
On the network shown in Figure 1, before the VPN ORF capability is enabled, the RR advertises all the VPN routes received from the VPN instances on PE1 to PE2. However, only the IRT 1:1 in these routes matches the ERT 1:1 of PE2. Similarly, the RR also advertises all the VPN routes received from the VPN instances on PE2 to PE1, and only the IRT 1:1 in these routes matches the ERT 1:1 of PE1. In this case, PE1 and PE2 both receive many unwanted routes. To prevent this issue, you can establish VPN ORF route-based peer relationships between the RR and PE1 and between the RR and PE2 in the BGP-VPN-Target address family. The VPN ORF route-based peers negotiate the VPN ORF capability. Then, PE1 and PE2 send VPN ORF routes to their peer (the RR). These VPN ORF routes carry the IRTs of the expected routes and original AS numbers. Based on the received routes, the RR constructs an export policy. The RR learns the routes matching the ERTs 1:1 and 2:2 from PE1 and the routes matching the ERTs 1:1 and 3:3 from PE2. Subsequently, because PE1 and PE2 require the same IRT, the RR sends only the routes with the IRT 1:1 to PE1 and PE2.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring VPN ORF, complete the following tasks:
Configure a basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN and establish VPNv4 connections.
Procedure
- Perform the following steps on each PE:
- Perform the following steps on the device that is to function as an RR:
Verifying the Configuration
After VPN ORF is enabled, run the display bgp vpn-target routing-table command to check routing information in the BGP VT address family.
Run the display bgp vpnv4 routing-table command to check information about BGP VPNv4 and BGP VPN routes.