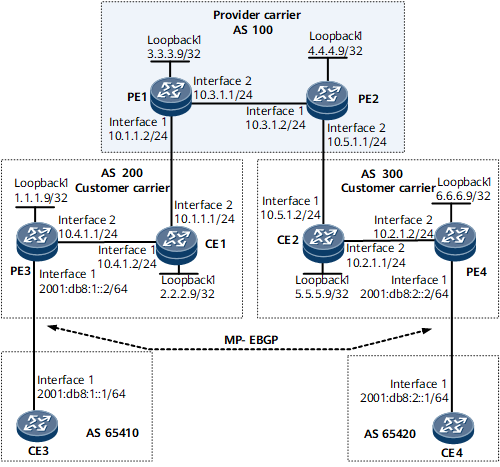
Example for Configuring the Carrier's Carrier (Inter-AS)
This section provides an example showing how a Level 2 carrier provides BGP/MPLS IPv6 VPN services when the Level 2 carrier and the Level 1 carrier are in different ASs.
Networking Requirements
As shown in Figure 1, the Level 1 carrier and the Level 2 carrier are in different ASs. The Level 2 carrier provides BGP/MPLS IPv6 VPN service for its customers.
The only difference from section Example for Configuring Carrier's Carrier in a Same AS is that the Level 1 carrier and the Level 2 carrier in this example are in different ASs.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
The two types of routes are exchanged as follows:
The exchange of the internal routes of the Level 2 carrier on the backbone network of Level 1 carrier: configuring the Level 2 carrier to access the Level 1 carrier as the Level 1 carrier's CE
The exchange of the external routes of the Level 2 carrier between the PE devices of the Level 2 carrier: setting up the MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PE devices (PE3 and PE4) of the Level 2 carrier
The Level 1 carrier's PEs and CEs are in different ASs. To distribute labels for the routes that are exchanged with CEs, the labeled MP-EBGP needs to be established between the CEs and PEs.
Data Preparation
To configure the inter-AS carrier's carrier, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR-ID on the PE and CE of the Level 1 carrier, MPLS LSR-IDs on the PE of the Level 2 carrier
Data for configuring IGP
Name of the VPN instance enable with IPv4 address family configured on the Level 1 carrier PE, RD and VPN targets
Name of the VPN instance enable with IPv6 address family configured on the Level 2 carrier PE, RD and VPN targets
Two route-policies configured on the CE of the Level 1 carrier
Procedure
- Configure BGP/MPLS IP VPN on the Level 1 carrier backbone network, using IS-IS as IGP of the backbone network. Enable LDP between PE1 and PE2, and establish MP-IBGP peer relationship.
The configuration procedures are similar to those in Example for Configuring Carrier's Carrier in a Same AS, and the specific configuration procedures are not mentioned here.

During the IGP configuration, the Loopback interface address in 32-bit of each PE needs to be advertised.
- Configure the Level 2 carrier network. Use OSPF as an IGP. Enable LDP between PE3 and CE1, and between PE4 and CE2 respectively.
The configuration procedures are similar to those in Example for Configuring Carrier's Carrier in a Same AS and not mentioned here.

During the IGP configuration, the loopback interface addresses with a 32-bit mask of each PE and CE needs to be advertised.
- Configure the Level 1 carrier CE to access the Level 1 carrier PE. Configure the exchange of labeled IPv4 routes between them.
# Configure CE1 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with PE3 and PE1.
<CE1> system-view [~CE1] interface gigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*CE1] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*CE1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*CE1-route-policy] quit [*CE1] route-policy policy2 permit node 1 [*CE1-route-policy] if-match mpls-label [*CE1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*CE1-route-policy] quit [*CE1] bgp 200 [*CE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 200 [*CE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*CE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 route-policy policy2 export [*CE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 label-route-capability [*CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 route-policy policy1 export [*CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 label-route-capability [*CE1-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*CE1-bgp] commit [~CE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE1 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with CE1.
<PE1> system-view [~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] apply-label per-route [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 1:1 both [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*PE1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*PE1-route-policy] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 route-policy policy1 export [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 label-route-capability [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE3 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with CE1.
<PE3> system-view [~PE3] bgp 200 [*PE3-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 200 [*PE3-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE3-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 label-route-capability [*PE3-bgp] commit [~PE3-bgp] quit
After the above configuration, the BGP peer relationship is established between CE1 and PE3, and between CE1 and PE1.
[~CE1] display bgp peer BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.9 Local AS number : 200 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 1.1.1.9 4 200 7 8 0 00:04:07 Established 0 10.1.1.2 4 100 3 4 0 00:00:08 Established 0
The configuration procedures of PE4, CE2 and PE2 are similar to those of PE3, CE1 and PE1, and are not mentioned here.
- Configure the Level 2 carrier's customers to access the Level 2 carrier PE.
The specific configuration procedures are the same as those in Example for Configuring Carrier's Carrier in a Same AS and are not mentioned here.
- Establish MP-EBGP peer relationship between the Level 2 carrier PEs to exchange VPN routes of the Level 2 carrier's customers.
# Configure PE3.
<PE3> system-view [~PE3] bgp 200 [*PE3-bgp] peer 6.6.6.9 as-number 300 [*PE3-bgp] peer 6.6.6.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE3-bgp] peer 6.6.6.9 ebgp-max-hop 10 [*PE3-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [*PE3-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 6.6.6.9 enable [*PE3-bgp-af-vpnv6] commit [~PE3-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [~PE3-bgp] quit
# Configure PE4.
<PE4> system-view [~PE4] bgp 300 [*PE4-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 200 [*PE4-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE4-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 ebgp-max-hop 10 [*PE4-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [*PE4-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [**PE4-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [*PE4-bgp] commit [~PE4-bgp] quit
- Verifying the configuration.
After the configuration, run the display ip routing-table command on PE1 and PE2 to see that the public routing table contains only the routes of the Level 1 carrier network. The following example uses the command output of PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 7 Routes : 7 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 3.3.3.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 4.4.4.9/32 ISIS 15 10 D 10.3.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.3.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.3.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.3.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.3.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.3.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command on PE1 and PE2 to see that the VPN routing table does not contain internal routes of the Level 2 carrier. The following example uses the command output of PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: vpn1 Destinations : 11 Routes : 11 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 EBGP 255 10 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 2.2.2.9/32 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 5.5.5.9/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 6.6.6.9/32 IBGP 255 10 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.0/24 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.5.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.5.1.2/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8
Run the display ip routing-table command on CE1 and CE2 to find that the public routing table contains internal routes of the Level 2 carrier. The following example uses the command output of CE1.
[~CE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 15 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.4.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 2.2.2.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 5.5.5.9/32 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 6.6.6.9/32 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.4.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.4.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.0/24 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.5.1.0/24 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.5.1.2/32 EBGP 255 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display ip routing-table command on PE3 and PE4 to find that the public routing table contains the internal routes of the Level 2 carrier. The following example uses the command output of PE3.
[~PE3] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 14 Routes : 14 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 2.2.2.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 5.5.5.9/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 2.2.2.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 6.6.6.9/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 2.2.2.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.4.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.0/24 EBGP 255 0 RD 6.6.6.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.1/32 EBGP 255 0 RD 6.6.6.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 2.2.2.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.5.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 2.2.2.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.5.1.2/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 2.2.2.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Running the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance command on PE3 and PE4 to see that the external routes of the Level 2 carrier are contained in the VPN routing table. The following example uses the command output of PE3.
[~PE3] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 Routing Table : vpn1 Destinations : 4 Routes : 4 Destination : 2001:db8:1:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:1::2 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthetnet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:db8:1::2 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthetnet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:db8:2:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : ::FFFF:6.6.6.9 Preference : 255 Cost : 0 Protocol : EBGP RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0xf0010060 Interface : NULL0 Flags : RD Destination : FE80:: PrefixLength : 10 NextHop : :: Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : NULL0 Flags : D
PE3 and PE4 can ping through each other.
[~PE3] ping 10.2.1.2 PING 10.2.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.2.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=251 time=116 ms Reply from 10.2.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=251 time=92 ms Reply from 10.2.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=251 time=118 ms Reply from 10.2.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=251 time=103 ms Reply from 10.2.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=251 time=121 ms --- 10.2.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 92/110/121 msCE3 and CE4 can ping through each other.
[~CE3] ping ipv6 2001:db8:2::1 PING 2001:db8:2::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 2001:db8:2::1 bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=62 time = 140 ms Reply from 2001:db8:2::1 bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=62 time = 141 ms Reply from 2001:db8:2::1 bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=62 time = 141 ms Reply from 2001:db8:2::1 bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=62 time = 140 ms Reply from 2001:db8:2::1 bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=62 time = 156 ms --- 2001:db8:2::1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 140/143/156 ms
Configuration Files
CE3 configuration file
# sysname CE3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 # ipv6 # bgp 65410 router-id 10.10.10.10 peer 2001:db8:1::2 as-number 200 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2001:db8:1::2 enable # returnPE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # ipv6 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 200 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 6.6.6.9 as-number 300 peer 6.6.6.9 ebgp-max-hop 10 peer 6.6.6.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable peer 2.2.2.9 label-route-capability peer 6.6.6.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 6.6.6.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 2001:db8:1::1 as-number 65410 import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 200 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospf 1 peer 10.1.1.2 enable peer 10.1.1.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.1.1.2 label-route-capability peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 1.1.1.9 route-policy policy2 export peer 1.1.1.9 label-route-capability # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label route-policy policy2 permit node 2 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 100 peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 4.4.4.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 4.4.4.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200 peer 10.1.1.1 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.1.1.1 label-route-capability import-route direct # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:2 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.5.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 10.5.1.2 as-number 300 peer 10.5.1.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.5.1.2 label-route-capability import-route direct # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.5.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 300 peer 10.5.1.1 as-number 100 peer 6.6.6.9 as-number 300 peer 6.6.6.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospf 1 peer 10.5.1.1 enable peer 10.5.1.1 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.5.1.1 label-route-capability peer 6.6.6.9 enable peer 6.6.6.9 route-policy policy2 export peer 6.6.6.9 label-route-capability # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label route-policy policy2 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE4 configuration file
# sysname PE4 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:2 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # ipv6 # mpls lsr-id 6.6.6.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 6.6.6.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 300 peer 5.5.5.9 as-number 300 peer 5.5.5.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 200 peer 1.1.1.9 ebgp-max-hop 10 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 5.5.5.9 enable peer 5.5.5.9 label-route-capability peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 6.6.6.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 2001:db8:2::1 as-number 65420 import-route direct # return
CE4 configuration file
# sysname CE4 # ipv6 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/64 # bgp 65420 router-id 20.20.20.20 peer 2001:db8:2::2 as-number 300 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2001:db8:2::2 enable # return