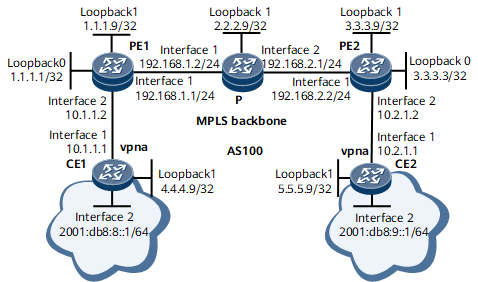
Example for Configuring 6VPE
With the 6VPE function, separate IPv6 networks belonging to the same VPN instance can be connected using an LSP.
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE2 belong to a VPN instance named vpna. If you want to implement communication between the IPv6 networks belong to vpna through an IPv4 network and shield the VPN IPv6 routes on the PEs over the IPv4 network, you can configure the 6VPE function.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP over the IPv4 backbone network to implement communication between PEs.
Configure MPLS and MPLS LDP on each PE and the P to establish an LDP LSP between the PEs.
Configure MP-IBGP on PE1 and PE2 to enable PEs to exchange IPv6 VPN routing information through BGP.
Configure a VPN instance that supports the IPv4 and IPv6 address families on each PE and bind the VPN instance to the PE interface connecting to a CE.
Configure BGP VPN peer relationships between PEs and CEs (tunnel forwarding).
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
AS numbers of PEs and CEs
VPN instance name
Attributes of the VPN instance IPv4 and IPv6 address families, such as RDs and route targets
Procedure
- Assign an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to each device interface.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an IGP over the IPv4 backbone network to implement communication between PEs. IS-IS is used in this example.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP on each device and device interface over the IPv4 backbone network. Create an LDP LSP between PE1 and PE2.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Set up a BGP VPNv6 peer relationship between the PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
After completing the preceding configuration, run the display bgp vpnv6 all peer command on each PE to check information about the BGP VPNv6 peer relationship. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp vpnv6 all peer BGP local router ID : 192.168.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.9 4 100 4 3 0 00:01:50 Established 0The command output shows that State is Established, indicating that the BGP VPNv6 peer relationship between PE1 and PE2 has been established.
- On each PE, configure a VPN instance that supports the IPv4 and IPv6 address families and bind the VPN instance to the PE interface connecting to a CE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 1:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:2 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 2:2 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] interface Loopback 0 [*PE1-LoopBack0] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-LoopBack0] quit [*PE1] commit
Repeat this step for PE2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure VPN peer relationships between PEs and CEs (tunnel forwarding).
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-mpls-ldp-vpn-instance-vpna] lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1] ospf 1 vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE1-ospf-1] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-instance-vpna] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp-instance-vpna] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*PE1-bgp-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] peer 4.4.4.9 enable [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] peer 4.4.4.9 label-route-capability [*PE1] commit
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [*CE1] mpls [*CE1-mpls] mpls ldp [*CE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*CE1] ospf 1 [*CE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*CE1-ospf-1] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*CE1] bgp 100 [*CE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*CE1-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] network 2001:DB8:8:: 64 [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit
The configurations of PE2 and CE2 are similar to those of PE1 and CE1, respectively. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the preceding configuration, CE1 and CE2 can learn IPv6 routes from each other and they can ping each other with ping packets carrying the source IP address. The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[~CE1] display ipv6 routing-table Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 7 Routes : 7 Destination : ::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : ::FFFF:127.0.0.0 PrefixLength : 104 NextHop : ::FFFF:127.0.0.1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : ::FFFF:127.0.0.1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:8:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:8::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : LoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:8::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : LoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:9:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : ::FFFF:1.1.1.1 Preference : 255 Cost : 0 Protocol : IBGP RelayNextHop : ::FFFF:10.1.1.2 TunnelID : 0x0000000001004c4b42 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : RD Destination : FE80:: PrefixLength : 10 NextHop : :: Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : NULL0 Flags : DB [~CE1] ping ipv6 -a 2001:db8:8::1 2001:db8:9::1 PING 2001:db8:9::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 2001:db8:9::1 bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=62 time = 170 ms Reply from 2001:db8:9::1 bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=62 time = 140 ms Reply from 2001:db8:9::1 bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=62 time = 150 ms Reply from 2001:db8:9::1 bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=62 time = 140 ms Reply from 2001:db8:9::1 bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=62 time = 170 ms --- 2001:db8:9::1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 140/154/170 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:2 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # mpls ldp vpn-instance vpna lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # isis 1 network-entity 10.1111.1111.1111.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # vpn-instance vpna peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 100 peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna peer 4.4.4.9 enable peer 4.4.4.9 label-route-capability # ospf 1 vpn-instance vpna area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 20.2222.2222.2222.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:2 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # mpls ldp vpn-instance vpna lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # isis 1 network-entity 30.3333.3333.3333.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable # vpn-instance vpna peer 5.5.5.9 as-number 100 peer 5.5.5.9 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct peer 5.5.5.9 enable peer 5.5.5.9 label-route-capability # ospf 1 vpn-instance vpna area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:8::1/64 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization network 2001:DB8:8:: 64 peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:9::1/64 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization network 2001:DB8:9:: 64 peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 label-route-capability # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return