Example for Configuring CC and CV for a Bidirectional LSP
This section provides an example for configuring continuity check (CC) and connectivity verification (CV) for a bidirectional label switched path (LSP).
Networking Requirements
- LSRA and LSRC serve as MEPs.
- LSRB serves as a MIP.
CC detects loss of continuity (LOC) between any MEPs in a maintenance entity group (MEG). A MEP sends continuity check messages (CCMs) to its remote MEP (RMEP) at a specified interval. If the RMEP does not receive CCMs within a period of 3.5 times as long as the specified interval, the RMEP considers that the connectivity between the MEPs has errors, reports an alarm, and enters the Down state. After that, automatic protection switching (APS) is triggered on both MEPs. Upon receipt of a CCM from the MEP, the RMEP clears the alarm and exits from the Down state.
CV enables a MEP to report alarms when receiving unexpected packets. For example, if a CV-enabled device receives a packet from an LSP and finds that this packet is incorrectly transmitted through the LSP, the device will report an alarm indicating a forwarding error.
Transport networks have strict requirements on the correctness of data forwarding. In addition, MPLS-TP requires that the data plane should be able to work without IP support, which means that packet forwarding is based on label switching only. Therefore, the correctness of label-based forwarding must be ensured.

Interfaces 1 through 2 in this example are GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/8, respectively.
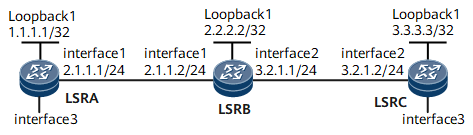
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
LSRA |
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2.1.1.1/24 |
|
LSRB |
Loopback1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2.1.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
3.2.1.1/24 |
|
LSRC |
Loopback1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
3.2.1.2/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create a maintenance entity (ME) instance and bind it to a bidirectional LSP.
(Optional) Configure an interval at which CCMs are sent and a priority for CCMs.
Enable CC and CV.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MEG name
Name of the tunnel interface to which an ME instance is bound
Interval at which CCMs are sent and priority of CCMs
Procedure
- Configure a bidirectional LSP.
For configuration details, see "Example for Configuring a Static Bidirectional Co-routed CR-LSP" in HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F SeriesRouter Configuration Guide - MPLS or "Configuration Files" in this section.
- Create an ME instance and bind it to the bidirectional LSP.# Create an ME instance named test on LSRA and bind it to Tunnel 10.
[~LSRA] mpls-tp meg test [~LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] me te interface Tunnel 10 mep-id 1 remote-mep-id 2 [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
# Create an ME instance named test on LSRC and bind it to Tunnel 20.[~LSRC] mpls-tp meg test [~LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] me te interface Tunnel 20 mep-id 2 remote-mep-id 1 [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
- (Optional) Configure an interval at which CCMs are sent and a priority for CCMs.

The same interval at which CCMs are sent and priority of CCMs must be configured on the MEP and RMEP. If the configurations at both ends are different, an alarm indicating an error is reported.
# Set the interval at which CCMs are sent to 100 ms and the priority of CCMs to 6 on LSRA.[~LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc interval 100 [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc exp 6 [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
# Set the interval at which CCMs are sent to 100 ms and the priority of CCMs to 6 on LSRC.[~LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc interval 100 [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc exp 6 [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
- Enable CC and CV.# Enable CC and CV on LSRA.
[~LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc send enable [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc receive enable [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] return
# Enable CC and CV on LSRC.[~LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc send enable [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] cc receive enable [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configurations, run the display mpls-tp oam meg command on LSRA to view MEG information.
<LSRA> display mpls-tp oam meg test -------------------------------------------------- MEG test -------------------------------------------------- meg name : test me count : 1 cc send : enable cc receive : enable cc interval : 100 cc exp : 6 ais : disable ais interval : 1000 ais exp : 7 lm single-end receive : disable lm dual-end : enable lm dual-end SD1 threshold: 1 lm dual-end SD2 threshold: 10 -------------------------------------------------- [ME 1] index : 0 direction : dual mep id : 1 remote mep id : 2 status board : 1 service type : te (cr-static-lsp) tunnel-name : Tunnel10 lsp name : state : UP alarm indicate : no alarm --------------------------------------------------
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp ingress Tunnel10 forward nexthop 2.1.1.2 out-label 20 backward in-label 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te bidirectional # ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.2 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.2 # mpls-tp meg test me te interface Tunnel10 mep-id 1 remote-mep-id 2 cc interval 100 cc exp 6 cc send enable cc receive enable # returnLSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp transit lsp1 forward in-label 20 nexthop 3.2.1.2 out-label 40 backward in-label 16 nexthop 2.1.1.1 out-label 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 3.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.1 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.2 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 forward in-label 40 lsrid 1.1.1.1 tunnel-id 100 backward nexthop 3.2.1.1 out-label 16 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 3.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel20 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.1 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 200 mpls te passive-tunnel mpls te binding bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.1 ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.1 # mpls-tp meg test me te interface Tunnel20 mep-id 2 remote-mep-id 1 cc interval 100 cc exp 6 cc send enable cc receive enable # return