Example for Configuring LB for a Bidirectional LSP
This section provides an example for configuring loopback (LB) for a bidirectional LSP.
Networking Requirements
- LSRA and LSRC serve as MEPs.
- LSRB serves as a MIP.
Reachability of the RMEP
Round-trip delay in the communication between the MEP and RMEP
Loss of ping packets between the MEP and RMEP

LB counts only the ping packets that are lost after being sent out, providing a rough packet loss ratio of the link between MEPs. The LM function can be used to obtain the accurate packet loss ratio of the link between MEPs.

Interfaces 1 through 2 in this example are GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/8, respectively.
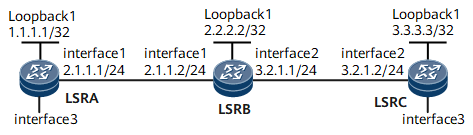
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
LSRA |
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2.1.1.1/24 |
|
LSRB |
Loopback1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2.1.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
3.2.1.1/24 |
|
LSRC |
Loopback1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
3.2.1.2/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create an ME instance and bind it to a bidirectional LSP.
Enable LB.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MEG name
Name of the tunnel interface to which an ME instance is bound
Procedure
- Configure a bidirectional LSP.
For configuration details, see "Example for Configuring a Static Bidirectional Co-routed CR-LSP" in HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F SeriesRouter Configuration Guide - MPLS or "Configuration Files" in this section.
- Create an ME instance and bind it to the bidirectional LSP.# Create an ME instance named test on LSRA and bind it to Tunnel 10.
[~LSRA] mpls-tp meg test [~LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] me te interface Tunnel 10 mep-id 1 remote-mep-id 2 [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
# Create an ME instance named test on LSRC and bind it to Tunnel 20.[~LSRC] mpls-tp meg test [~LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] me te interface Tunnel 20 mep-id 2 remote-mep-id 1 [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-test] commit
- Enable LB.

LB can be used to monitor the connectivity between a MEP and its RMEP or a MIP. In this example, LB is used to monitor the connectivity between LSRA and LSRC.
Enable LB on LSRA.<LSRA> ping meg test PING test: 9 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from test: bytes=9, Sequence=1 time=100 ms Reply from test: bytes=9, Sequence=2 time=90 ms Reply from test: bytes=9, Sequence=3 time=100 ms Reply from test: bytes=9, Sequence=4 time=90 ms Reply from test: bytes=9, Sequence=5 time=100 ms --- ping statistics --- 5 packet (s) transmitted 5 packet (s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max 90/96/100 ms
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp ingress Tunnel10 forward nexthop 2.1.1.2 out-label 20 backward in-label 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te bidirectional # ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.2 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.2 # mpls-tp meg test me te interface Tunnel10 mep-id 1 remote-mep-id 2 # returnLSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp transit lsp1 forward in-label 20 nexthop 3.2.1.2 out-label 40 backward in-label 16 nexthop 2.1.1.1 out-label 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 3.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.1 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.2 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 forward in-label 40 lsrid 1.1.1.1 tunnel-id 100 backward nexthop 3.2.1.1 out-label 16 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 3.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel20 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.1 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 200 mpls te passive-tunnel mpls te binding bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.1 ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.1 # mpls-tp meg test me te interface Tunnel20 mep-id 2 remote-mep-id 1 # return