Example for Configuring MVPN Extranet in the Remote Route Leaking Scenario Where a Source VPN Instance Needs to Be Configured on a Receiver PE
This section provides an example for configuring MVPN extranet in the remote route leaking scenario where a source VPN instance needs to be configured on a receiver PE.
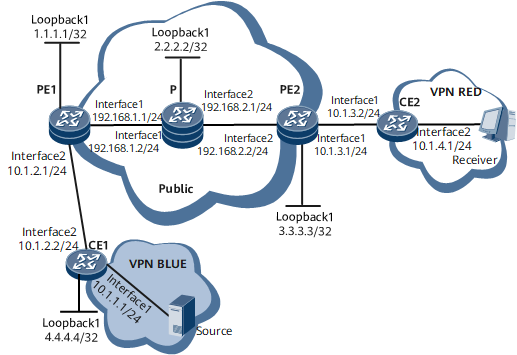
Networking Requirements
MD MVPN supports only intra-VPN multicast service distribution. In real-world application, however, a service provider may need to provide multicast services to users in a different VPN than its own VPN. This requires inter-VPN multicast distribution.
In the remote route leaking scenario of intra-AS MD MVPN shown in Figure 1, the receiver in VPN RED requires multicast data from the source in VPN BLUE. To meet this requirement, deploy MVPN extranet by configuring source VPN BLUE on receiver PE2. In addition, configure a multicast routing policy for VPN RED on receiver PE2 and specify in the policy that the upstream interface of the RPF route belongs to VPN BLUE.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic intra-AS MD MVPN functions.
Configure the VPN instance (VPN BLUE) enabled with the IPv4 address family on PE2 and bind the VPN instance to an MTunnel interface.
Configure Rendezvous Points (RPs) to serve the public network.
Configure RPs to serve the multicast groups running the multicast VPN extranet service.
Configure a multicast routing policy for VPN RED on PE2 and specify VPN BLUE as the upstream interface of the RPF route.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
RD and RT of VPN BLUE: 100:1
RD and RT of VPN RED: 200:1
Share-group address of VPN BLUE: 239.0.0.0
Share-group address of VPN RED: 238.0.0.0
Procedure
- Configure basic intra-AS MD MVPN functions.
- Configure VPN BLUE on PE2 and bind VPN BLUE to MTunnel 0.
[~PE2] ip vpn-instance BLUE [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE-af-ipv4] vpn-target 100:1 both [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE-af-ipv4] multicast-domain share-group 239.0.0.0 binding mtunnel 0 [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-BLUE] quit [*PE2] commit [~PE2] interface MTunnel 0 [*PE2-MTunnel0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [*PE2-MTunnel0] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure an RP to serve the public network.
[~P] pim [*P-pim] c-bsr Loopback 1 [*P-pim] c-rp Loopback 1 [*P-pim] quit [*P] commit
- Configure an RP to serve the multicast groups running the multicast VPN extranet service.

Source VPN instances and receiver VPN instances support only static RPs. In addition, the routes to static RPs and the routes to the sources need to be in the same VPN instance.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] pim [*CE1-pim] static-rp 4.4.4.4 [*CE1-pim] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] pim vpn-instance BLUE [*PE1-pim-BLUE] static-rp 4.4.4.4 [*PE1-pim-BLUE] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] pim vpn-instance BLUE [*PE2-pim-BLUE] static-rp 4.4.4.4 [*PE2-pim-BLUE] quit [*PE2] pim vpn-instance RED [*PE2-pim-RED] static-rp 4.4.4.4 [*PE2-pim-RED] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] pim [*CE2-pim] static-rp 4.4.4.4 [*CE2-pim] quit [*CE2] commit
- Configure a multicast routing policy for VPN RED, specifying that the upstream interface of the RPF route selected by the PIM entry with the group address 228.1.1.0/24 belongs to VPN BLUE.
[~PE2] ip vpn-instance RED [*PE2-vpn-instance-RED] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-RED-af-ipv4] multicast extranet select-rpf vpn-instance BLUE group 228.0.0.0 24 [*PE2-vpn-instance-RED-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-RED] quit [*PE2] commit
- Verify the configuration.
By checking the configuration result, you can view that the receiver in VPN RED can receive multicast data from the source in VPN BLUE.
Run the display pim routing-table command on PE2 to check information about the PIM routing table. The following command output shows that the upstream interface of the RPF route selected by the PIM entry with the group address 228.0.0.1 belongs to VPN BLUE.
[~PE2] display pim vpn-instance RED routing-table extranet source-vpn-instance vpn-instance BLUE VPN-Instance: RED Total 1 (*, G) entry; 2 (S, G) entries Total matched 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, 228.0.0.1) RP: 4.4.4.4 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:47:55 Upstream interface: MCAST_Extranet(BLUE) Upstream neighbor: 1.1.1.1 RPF prime neighbor: 1.1.1.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:47:55, Expires: 00:02:34 (10.1.1.2, 228.0.0.1) RP: 4.4.4.4 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT UpTime: 06:18:43 Upstream interface: MCAST_Extranet(BLUE) Upstream neighbor: 1.1.1.1 RPF prime neighbor: 1.1.1.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:47:57, Expires: 00:02:32
The following command output shows that the MVPN extranet receiver of VPN BLUE belongs to VPN RED.
[~PE2] display pim vpn-instance BLUE routing-table extranet receive-vpn-instance vpn-instance RED VPN-Instance: BLUE Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry Total matched 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, 228.0.0.1) RP: 4.4.4.4 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC EXTRANET UpTime: 00:06:27 Upstream interface: MTunnel0 Upstream neighbor: 1.1.1.1 RPF prime neighbor: 1.1.1.1 Downstream interface(s) information: none Extranet receiver(s): 1 1: RED (10.1.1.2, 228.0.0.1) RP: 4.4.4.4 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT EXTRANET UpTime: 00:06:06 Upstream interface: MTunnel0 Upstream neighbor: 1.1.1.1 RPF prime neighbor: 1.1.1.1 Downstream interface(s) information: none Extranet receiver(s): 1 1: REDRun the display multicast routing-table command on PE2 to check information about the multicast routing table. The following command output shows that the upstream interface of the RPF route selected by the multicast routing entry with the group address 228.0.0.1 belongs to VPN BLUE.
[~PE2] display multicast vpn-instance RED routing-table extranet source-vpn-instance vpn-instance BLUE Multicast routing table of VPN instance: RED Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry, 1 matched 00001: (10.1.1.2, 228.0.0.1) Uptime: 00:42:23 Upstream Interface: MCAST_Extranet(BLUE) List of 1 downstream interface 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0
Run the display multicast rpf-info command on PE2 to check the RPF routing information of source 10.1.1.2. The following command output shows that the upstream interface of the RPF route selected by the multicast routing entry with the group address 228.0.0.1 belongs to VPN BLUE.
[~PE2] display multicast vpn-instance RED rpf-info 10.1.1.2 228.0.0.1 VPN-Instance: RED RPF information about source 10.1.1.2 and group 228.0.0.1 RPF interface: MCAST_Extranet RPF Source VPN-Instance: BLUE Referenced route/mask: 10.1.1.0/24 Referenced route type: unicast Route selection rule: preference-preferred Load splitting rule: disableAfter the preceding configurations, Receiver can receive multicast data from Source. Run the display pim routing-table command on CE2 to check information about the PIM routing table. The following command output shows that multicast data has reached CE2 and forwarded to Receiver.
[~CE2] display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, 228.0.0.1) RP: 4.4.4.4 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:53:02 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:53:02 Upstream neighbor: 10.1.3.1 RPF prime neighbor: 10.1.3.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: static, UpTime: 00:53:02, Expires: - (10.1.1.2, 228.0.0.1) RP: 4.4.4.4 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT UpTime: 00:08:02 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:08:02 Upstream neighbor: 10.1.3.1 RPF prime neighbor: 10.1.3.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:08:02, Expires: -
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # multicast routing-enable # ip vpn-instance BLUE ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable multicast-domain share-group 239.0.0.0 binding mtunnel 0 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance BLUE ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 pim sm # interface MTunnel0 ip binding vpn-instance BLUE ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance BLUE import-route direct import-route ospf 2 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf 2 vpn-instance BLUE import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 # pim # pim vpn-instance BLUE static-rp 4.4.4.4 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # multicast routing-enable # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 pim sm # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # pim c-bsr LoopBack1 c-rp LoopBack1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # multicast routing-enable # ip vpn-instance BLUE ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable multicast-domain share-group 239.0.0.0 binding mtunnel 0 # ip vpn-instance RED ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable multicast-domain share-group 238.0.0.0 binding mtunnel 1 multicast extranet select-rpf vpn-instance BLUE group 228.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance RED ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 pim sm # interface MTunnel0 ip binding vpn-instance BLUE ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface MTunnel1 ip binding vpn-instance RED ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance BLUE import-route direct import-route ospf 2 # ipv4-family vpn-instance RED import-route direct import-route ospf 2 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf 2 vpn-instance RED import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # pim # pim vpn-instance RED static-rp 4.4.4.4 # pim vpn-instance BLUE static-rp 4.4.4.4 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 pim sm # ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 # pim static-rp 4.4.4.4 # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo portswitch undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable igmp static-group 228.0.0.1 # ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.4.0 0.0.0.255 # pim static-rp 4.4.4.4 # return