Example for Configuring OSPF IP FRR
This section describes how to configure OSPF IP FRR with an example, including how to block FRR on certain interfaces to prevent the links connected to these interfaces from functioning as backup links and how to bind OSPF IP FRR to a BFD session.
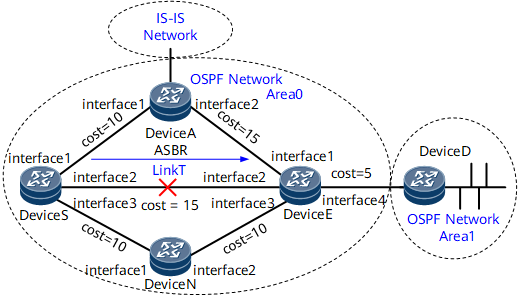
Networking Requirements
- It takes hundreds of milliseconds for the traffic to be switched to a backup link. During this period, services are interrupted.
- Traffic may be switched to the link that passes through Device A. Device A is an ASBR and is not expected to function as a backup device.
If a fault occurs on the network, OSPF IP FRR can fast switch traffic to the backup link without waiting for route convergence. This ensures uninterrupted traffic transmission. In addition, you can also prevent the link which passes through Device A from functioning as the FRR backup link.
- All routers run OSPF.
- The link cost meets the OSPF IP FRR traffic protection inequality.
If the primary link T fails, Device S immediately switches traffic to the backup link which passes through Device N.
- Based on the network planning, the link which passes through Device A does not function as an FRR backup link.
Precautions
When configuring OSPF IP FRR, note the following points:
Before configuring OSPF IP FRR, block FRR on certain interfaces to prevent the links connected to these interfaces from functioning as backup links. After that, the link where the interface resides is not calculated as a backup link during FRR calculation.
During the configuration of OSPF IP FRR, the lower layer needs to fast respond to a link change so that traffic can be rapidly switched to the backup link. After the bfd all-interfaces frr-binding command is run, the BFD session status is associated with the link status of an interface so that link faults can be rapidly detected.
Configuration Roadmap
Configure basic OSPF functions on each router.
Configure BFD for OSPF on all the devices in Area 0.
Set the costs of links to ensure that link T is selected to transmit traffic.
Block FRR on a specified interface of Device S.
- Enable OSPF IP FRR on Device S to protect the traffic forwarded by Device S.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data.
Device |
Router ID |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|
DeviceS |
1.1.1.1 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
GE0/1/8 |
10.1.2.1/24 |
||
GE0/1/16 |
10.1.3.1/24 |
||
DeviceA |
2.2.2.2 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
GE0/1/8 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
||
DeviceN |
3.3.3.3 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.3.2/24 |
GE0/1/8 |
10.2.3.2/24 |
||
DeviceE |
4.4.4.4 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
GE0/1/8 |
10.1.2.2/24 |
||
GE0/1/16 |
10.2.3.1/24 |
||
GE0/1/1 |
172.17.1.1/24 |
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic OSPF functions. For details, see Example for Configuring Basic OSPF Functions.
- Configure BFD for OSPF on all the devices in Area 0. For details, see Example for Configuring BFD for OSPF.
- Set the costs of links to ensure that link T is selected to transmit traffic.
# Configure Device S.
[~DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ospf cost 10 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ospf cost 15 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [~DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ospf cost 10 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceS] commit
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ospf cost 15 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure Device N.
[~DeviceN] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ospf cost 10 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceN] commit
- Block FRR on a specified interface of Device S.
[~DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ospf frr block [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceS] commit
- Enable OSPF IP FRR on Device S.
# Enable OSPF IP FRR on Device S.
[~DeviceS] ospf [*DeviceS-ospf-1] frr [*DeviceS-ospf-1-frr] loop-free-alternate [*DeviceS-ospf] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display ospf routing router-id command on Device S to view routing information.
[~DeviceS-ospf-1-frr] display ospf routing router-id 4.4.4.4 OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 1.1.1.1 Destination : 4.4.4.4 Route Type : Intra-area Area : 0.0.0.1 AdvRouter : 4.4.4.4 Type : ASBR URT Cost : 59 NextHop : 10.2.2.1. Interface : GE0/1/8 Backup Nexthop : 10.1.3.2 Backup Interface : GE0/1/16 Backup Type : LFA LINK
The preceding display shows that a backup route is generated on Device S.
Configuration Files
Device S configuration file
# sysname DeviceS # bfd # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ospf frr block ospf cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 15 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 10 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 bfd all-interfaces enable bfd all-interfaces frr-binding frr loop-free-alternate area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # bfd # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 15 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 bfd all-interfaces enable bfd all-interfaces frr-binding frr loop-free-alternate area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device N configuration file
# sysname DeviceN # bfd # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 10.2.3.2 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 10 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 bfd all-interfaces enable bfd all-interfaces frr-binding frr area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device E configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # bfd # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 ip address 10.2.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.255.0 ospf cost 5 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 router-id 4.4.4.4 bfd all-interfaces enable bfd all-interfaces frr-binding area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.17.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return