MTrace
A multicast trace route (MTrace) test instance monitors a multicast forwarding path from a multicast source to the current router or a destination host and collects statistics about routers along the multicast forwarding path.
MTrace is based on a multicast-enabled network, such as a Layer 3 multicast network that has Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) configured, Rosen MVPN, or NG MVPN.
A device sends an IGMP tracert query message to query the last-hop device on a multicast forwarding path.
An IGMP tracert request message completely inherits an IGMP tracert query message, with a response data block being added to the end of the message.
An IGMP tracert response message completely inherits an IGMP tracert request message, with only the message type field changed.
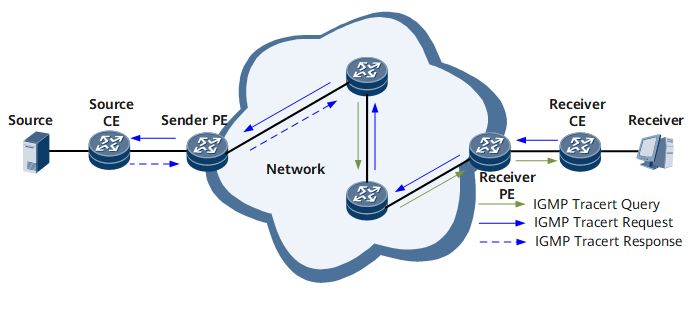
MTrace applies to the following scenarios.
An MTrace test instance detects a reverse path forwarding (RPF) path from a multicast source to the current router (when the current router is the last-hop multicast device to a destination host).
The current router queries the previous-hop device on the RPF path and sends an IGMP tracert request message to it.
After receiving the IGMP tracert request message, the previous-hop router adds a response data block containing information about the interface receiving this IGMP tracert request message and sends the message to its previous-hop router. The router of each hop adds a response data block to the IGMP tracert request message and sends the message upstream.
When the first-hop router connected with the multicast source receives the IGMP tracert request message, it also adds a response data block and sends an IGMP tracert response message to the current router.
After receiving the IGMP tracert response message, the current router parses it and obtains information about the RPF path from the multicast source to the destination host. This can clearly reflect the RPF path status.
If the IGMP tracert request message cannot reach the first-hop router because of some errors, an IGMP tracert response message is directly sent to the current router. The current router then parses the data block information to locate the faulty node. In this way, faulty node monitoring is implemented.
An MTrace test instance detects a multicast path from a multicast source to the current router (when the current router is the last-hop multicast device to a destination host).
The current router queries the previous-hop device on the multicast path and sends an IGMP tracert request message to it.
After receiving the IGMP tracert request message, the previous-hop router adds a response data block containing information about the interface receiving this IGMP tracert request message and sends the message to its previous-hop router. The router of each hop adds a response data block to the IGMP tracert request message and sends the message upstream.
When the first-hop router connected with the multicast source receives the IGMP tracert request message, it also adds a response data block and sends an IGMP tracert response message to the current router.
After receiving the IGMP tracert response message, the current router parses it and obtains information about the multicast path from the multicast source to the destination host. This can clearly reflect the multicast path status.
If the IGMP tracert request message cannot reach the first-hop router because of some errors, an IGMP tracert response message is directly sent to the current router. The current router then parses the data block information to locate the faulty node. In this way, faulty node monitoring is implemented.
An MTrace test instance detects an RPF path from a multicast source to a destination host (when the current router is not the last-hop multicast device to a destination host).
The current router sends an IGMP tracert query message to query the last-hop router connected with the destination host.
After receiving the IGMP tracert query message, the last-hop router adds a response data block containing its device information, constructs an IGMP tracert request message, and sends the message to its previous-hop router. The router of each hop adds a response data block to the IGMP tracert request message and sends the message upstream.
When the first-hop router connected with the multicast source receives the IGMP tracert request message, it also adds a response data block and sends an IGMP tracert response message to the current router.
After receiving the IGMP tracert response message, the current router parses it and obtains information about the RPF path from the multicast source to the destination host and each router on the path. This can clearly reflect the RPF path status and statistics of each router on the path.
If the IGMP tracert request message cannot reach the first-hop router because of some errors, an IGMP tracert response message is directly sent to the current router. The current router then parses the data block information to locate the faulty node. In this way, faulty node monitoring is implemented.
An MTrace test instance detects a multicast path from a multicast source to a destination host (when the current router is not the last-hop multicast device to a destination host).
The current router sends an IGMP tracert query message to query the last-hop router connected with the destination host.
After receiving the IGMP tracert query message, the last-hop router adds a response data block containing its device information, constructs an IGMP tracert request message, and sends the message to its previous-hop router. The router of each hop adds a response data block to the IGMP tracert request message and sends the message upstream.
When the first-hop router connected with the multicast source receives the IGMP tracert request message, it also adds a response data block and sends an IGMP tracert response message to the current router.
After receiving the IGMP tracert response message, the current router parses it and obtains information about the multicast path from the multicast source to the destination host and each router on the path. This can clearly reflect the multicast path status and statistics of each router on the path.
If the IGMP tracert request message cannot reach the first-hop router because of some errors, an IGMP tracert response message is directly sent to the current router. The current router then parses the data block information to locate the faulty node. In this way, faulty node monitoring is implemented.
- The unicast address of the last-hop router is known: The IP address of the last-hop router is set as the destination address of the message. The current router encapsulates a unicast IGMP tracert query message.
- The addresses of the last-hop router and destination host are unknown, but the current router directly connects to the destination host: 224.0.0.2 is set as the destination address of the message, and the TTL value is set to 1. The current router encapsulates an IGMP tracert query message and sends it to all routers on the same network segment to find the last-hop router.
- The address of the last-hop router is unknown but the unicast address of the destination host is known: The IP address of the destination host is set as the destination address of the message. The current router encapsulates an IGMP tracert query message. The message must contain the IP option Router Alert.
- The address of the last-hop router is unknown but the unicast address of the destination host is known, and the current router is in the multicast distribution tree: The multicast group address is set as the destination address, and the multicast source address is set as the source address. The current router encapsulates an IGMP tracert query message. The message is forwarded along the multicast or RPF path and finally arrives at the last-hop router.