Example for Configuring a QinQ VLAN Tag Termination Sub-Interface to Support Proxy ARP
This example shows how to configure a QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support proxy ARP, and how to enable the interworking between users who are on the same network segment but different VLANs.
Networking Requirements
A range of VLANs can connect to a network segment using VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces. However, if users on the same network segment belong to different VLANs, these users cannot communicate at Layer 2, and rely on IP forwarding at Layer 3 to communicate with each other. You can configure VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to support proxy ARP so that users from different VLANs can communicate.
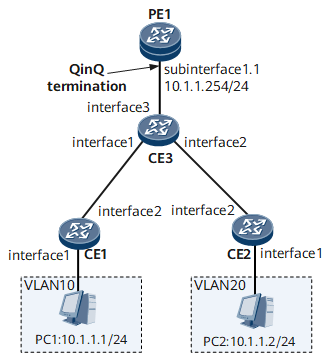
On the network shown in Figure 1, PE1 connects to CE3 through an Ethernet sub-interface; CE3 connects to CE1 and CE2 which connects to both PC1 and PC2. PC1 and PC2 belong to the same network segment but are on different VLANs. PC1 and PC2 have no default gateway. Packets received by PE1 carry two VLAN tags. In this situation, you can configure GE 0/1/1.1 on PE1 as a QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface and enable proxy ARP on the sub-interface so that PC1 and PC2 can communicate.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create VLANs on CE1 and CE2 and determine the VLANs to which users belong.
Configure the QinQ function on CE3 so that packets sent by CE3 to PE1 carry two VLAN tags.
Configure a QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface and enable proxy ARP on the sub-interface on PE1 so that users from different VLANs can communicate.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- VLAN ID in the outer VLAN tag of packets sent by CE3 to PE1.
- User VLAN IDs
- User IP addresses
- Names of interfaces that connect the CEs
- Names of interfaces that connect PE1 and CE3
- Names of interfaces that connect CE1 and CE2 to PCs
Procedure
- Create VLANs on CE1 and CE2 and associate the VLANs with Layer 2 interfaces.
# Configure CE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE1] vlan 10 [*CE1-vlan10] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 10 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type trunk [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure CE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE2] vlan 20 [*CE2-vlan20] quit [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 20 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type trunk [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE2] commit

If the interface is already a Layer 2 interface, do not run the portswitch command.
- Configure the QinQ function on CE3 so that packets sent by CE3 to PE1 carry two VLAN tags.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE3 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE3] vlan 100 [*CE3-vlan100] quit [*CE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 10 stack-vlan 100 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port vlan-stacking vlan 20 stack-vlan 100 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port link-type trunk [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit

If the device does not support the port vlan-stacking command, you can run the port link-type dot1q-tunnel command and port default vlan command on the interface to configure the QinQ function.
- Configure a QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface and enable proxy ARP on PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] control-vid 1 qinq-termination [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 10 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 20 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] ip address 10.1.1.254 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] arp-proxy inter-sub-vlan-proxy enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] arp broadcast enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE1] commit

When you run the qinq termination command on an interface, if the pe-vid values are the same, make sure that the ce-vid values of the sub-interfaces are different.
- Verify the configuration.
Verify that PC1 can ping PC2.
Check the ARP table on PC1. If the MAC address of PC1 is the MAC address of GE 0/1/1 on PE1, the configuration is correct.
Configuration Files
Configuration file of PE1
# sysname PE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 encapsulation qinq-termination qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 10 qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 20 ip address 10.1.1.254 255.255.255.0 arp-proxy inter-sub-vlan-proxy enable arp broadcast enable # return
Configuration file of CE3
# sysname CE3 # vlan batch 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port vlan-stacking vlan 10 stack-vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port vlan-stacking vlan 20 stack-vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # return
Configuration file of CE1
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown portswitch port link-type access port default vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown portswitch port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # return
Configuration file of CE2
# sysname CE2 # vlan batch 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown portswitch port link-type access port default vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown portswitch port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # return