Example for Configuring a Dot1q VLAN Tag Termination Sub-Interface to Support VRRP
This section describes how to ensure reliable and stable connections between users that send single-tagged packets and the network after you have configured a dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
Networking Requirements
To use VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to access a network with a VRRP group, enable VRRP on the sub-interfaces. VRRP can ensure reliable and stable communication between users on the network.
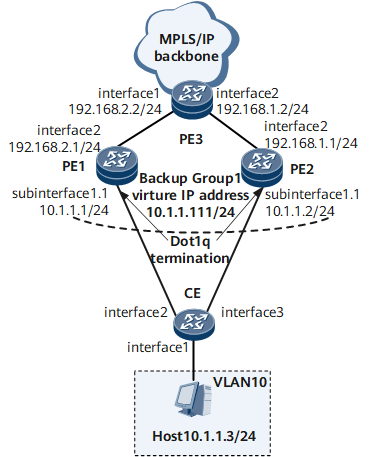
On the network shown in Figure 1, packets sent by the CE to PEs carry one VLAN tag, and the CE is connected to the network with VRRP groups through the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces on the PEs. To ensure that a master/backup VRRP switchover is performed immediately after a fault occurs on the network and that the communication is reliable and stable, configure dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to support VRRP.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create a VLAN on the CE and determine the VLAN to which users belong.
Configure the Layer 2 forwarding function on the CE so that packets sent by the CE to PE1 and PE2 carry one VLAN tag.
Deploy a VRRP group on PE1 and PE2 to implement link backup.
Configure dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces on PE1 and PE2 to support VRRP to ensure stable network communication.
Configure a routing protocol on PE1, PE2, and PE3 to ensure that users can access the carrier network on the Layer 3 network.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is used in this example.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- Users' VLAN IDs and IP addresses
- Names and IP addresses of the interfaces that connect PE1 and PE2 to the CE.
- Names and IP addresses of the interfaces that connect PE1 and PE2
- ID and virtual IP address of the VRRP group and priorities of PE1 and PE2 in the VRRP group
Procedure
- Create a VLAN on the CE and associate a Layer 2 interface with the VLAN.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE] vlan 10 [*CE-vlan10] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 10 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE] commit
- Configure Layer 2 forwarding on the CE.
[~CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type trunk [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE] commit [~CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port link-type trunk [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*CE] commit

If the interface is already a Layer 2 interface, do not run the portswitch command.
- Configure a VRRP group.
# Create VRRP group 1 on PE1, set the default gateway address to 10.1.1.111, and set the VRRP priority to 120 so that PE1 is the Master in VRRP group 1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.111 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vrrp vrid 1 priority 120 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 20 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vrrp recover-delay 20 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Create VRRP group 1 on PE2, and set the default gateway address to 10.1.1.111. (Do not set the VRRP priority so that PE2 is the Backup in VRRP group 1.)
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.111 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to support VRRP.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] control-vid 1 dot1q-termination [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] dot1q termination vid 10 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] dot1q vrrp vid 10 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] arp broadcast enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] control-vid 1 dot1q-termination [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] dot1q termination vid 10 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] dot1q vrrp vid 10 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] arp broadcast enable [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE2] commit
Run the display vrrp command on PE1. The command output shows that PE1 is in the master state. Run the display vrrp command on PE2. The command output shows that PE2 is in the Backup state. The command outputs are as follows:
[~PE1] display vrrp GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 | Virtual Router 1 State : Master Virtual IP : 10.1.1.111 Master IP : 10.1.1.1 Local IP : 10.1.1.1 PriorityRun : 120 PriorityConfig : 120 MasterPriority : 120 Preempt : YES Delay Time : 20s Hold Multiplier: 4 TimerRun : 1s TimerConfig : 1s Auth Type : NONE Virtual MAC : 00e0-fc12-3456 Check TTL : YES Config Type : normal-vrrp Create Time : 2012-07-18 09:53:03 Last Change Time : 2012-07-18 09:54:17 [~PE2] display vrrp GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 | Virtual Router 1 State : Backup Virtual IP : 10.1.1.111 Master IP : 10.1.1.1 Local IP : 10.1.1.2 PriorityRun : 100 PriorityConfig : 100 MasterPriority : 120 Preempt : YES Delay Time : 0s Hold Multiplier: 4 TimerRun : 1s TimerConfig : 1s Auth Type : NONE Virtual MAC : 00e0-fc12-3456 Check TTL : YES Config Type : normal-vrrp Create Time : 2012-07-18 09:53:00 Last Change Time : 2012-07-18 09:56:11
Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/1.1 of PE1 to simulate a situation in which PE1 is faulty.
Run the display vrrp command on PE1 and PE2 respectively to view the VRRP status. The command outputs show that the VRRP status of PE1 is Initialize and the VRRP status of PE2 is Master.
[*PE1] display vrrp GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 | Virtual Router 1 State : Initialize Virtual IP : 10.1.1.111 Master IP : 0.0.0.0 Local IP : 10.1.1.1 PriorityRun : 120 PriorityConfig : 120 MasterPriority : 0 Preempt : YES Delay Time : 20s Hold Multiplier: 4 TimerRun : 1s TimerConfig : 1s Auth Type : NONE Virtual MAC : 00e0-fc12-3456 Check TTL : YES Config Type : normal-vrrp Create Time : 2012-07-18 09:53:03 Last Change Time : 2012-07-18 10:03:03 [*PE2] display vrrp GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 | Virtual Router 1 State : Master Virtual IP : 10.1.1.111 Master IP : 10.1.1.2 Local IP : 10.1.1.2 PriorityRun : 100 PriorityConfig : 100 MasterPriority : 100 Preempt : YES Delay Time : 0s Hold Multiplier: 4 TimerRun : 1s TimerConfig : 1s Auth Type : NONE Virtual MAC : 00e0-fc12-3456 Check TTL : YES Config Type : normal-vrrp Create Time : 2012-07-18 09:53:00 Last Change Time : 2012-07-18 10:53:09
Run the undo shutdown command on GE 0/1/1.1 on PE1. After GE 0/1/1.1 goes Up, run the display vrrp command on PE1 to view the VRRP status. The command output shows that the VRRP status of PE1 is Backup.

- If no preemption delay is configured in VRRP group 1, the VRRP status of PE1 is Master immediately.
- If the preemption delay is configured in VRRP group 1, the VRRP status of PE1 is Master after 20 seconds.
[*PE1] display vrrp GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 | Virtual Router 1 State : Backup Virtual IP : 10.1.1.111 Master IP : 10.1.1.2 Local IP : 10.1.1.1 PriorityRun : 120 PriorityConfig : 120 MasterPriority : 100 Preempt : YES Delay Time : 20s Hold Multiplier: 4 TimerRun : 1s TimerConfig : 1s Auth Type : NONE Virtual MAC : 00e0-fc12-3456 Check TTL : YES Config Type : normal-vrrp Create Time : 2012-07-18 09:53:03 Last Change Time : 2012-07-18 10:54:35
After 20 seconds, run the display vrrp command on PE1 to view the VRRP status. The command output shows that the VRRP status of PE1 is Master.
[*PE1] display vrrp GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 | Virtual Router 1 State : Master Virtual IP : 10.1.1.111 Master IP : 10.1.1.1 Local IP : 10.1.1.2 PriorityRun : 120 PriorityConfig : 120 MasterPriority : 120 Preempt : YES Delay Time : 20s Hold Multiplier: 4 TimerRun : 1s TimerConfig : 1s Auth Type : NONE Virtual MAC : 00e0-fc12-3456 Check TTL : YES Config Type : normal-vrrp Create Time : 2012-07-18 09:53:03 Last Change Time : 2012-07-18 10:54:50
- Configure OSPF on the PEs.
Configure IP addresses of interfaces and OSPF on the PEs, as shown in Figure 1.
# Configure PE1.
[*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 192.168.2.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE1] ospf [*PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE1-ospf-1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 192.168.1.1 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE2] ospf [*PE2-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE2-ospf-1] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE3 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE3] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 192.168.2.2 24 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 192.168.1.2 24 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE3] ospf [*PE3-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE3-ospf-1] quit [*PE3] commit
After the configurations are complete, PE1 and PE2 can ping each other.
Use the command output on PE1 as an example.
[~PE1] ping 192.168.1.1 PING 192.168.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=140 ms Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=23 ms Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=56 ms Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=14 ms Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=4 ms --- 192.168.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 4/47/140 ms - Verify the configuration.
Run the display ip routing-table command on PE1 and PE2. Verify that the following conditions are true:
a. The command output shows that there is a direct route in the routing table of PE1.
b. The destination address of the direct route is a virtual IP address.
c. The route to the same destination address on PE2 is an OSPF route.
[*PE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 16 Routes : 16 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 10.1.1.111/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 OSPF 10 2 D 192.168.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 192.168.2.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 192.168.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 192.168.2.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 [~PE2] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 16 Routes : 16 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 10.1.1.111/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 192.168.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 192.168.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 192.168.2.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 OSPF 10 2 D 192.168.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation dot1q-termination dot1q termination vid 10 dot1q vrrp vid 10 arp broadcast enable vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.111 vrrp vrid 1 priority 120 vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 20 vrrp recover-delay 20 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 encapsulation dot1q-termination dot1q termination vid 10 dot1q vrrp vid 10 arp broadcast enable vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.111 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Configuration file of the CE
# sysname CE # vlan batch 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # return