Configuring an Inter-AS E2E SR-MPLS TE Tunnel (Path Computation on the Controller)
An inter-AS E2E SR-MPLS TE tunnel can connect SR-MPLS TE tunnels in multiple AS domains to build a large-scale TE network.
Usage Scenario
SR-MPLS TE, a new MPLS TE tunneling technology, has unique advantages in label distribution, protocol simplification, large-scale expansion, and fast path adjustment. SR-MPLS TE can better cooperate with SDN.
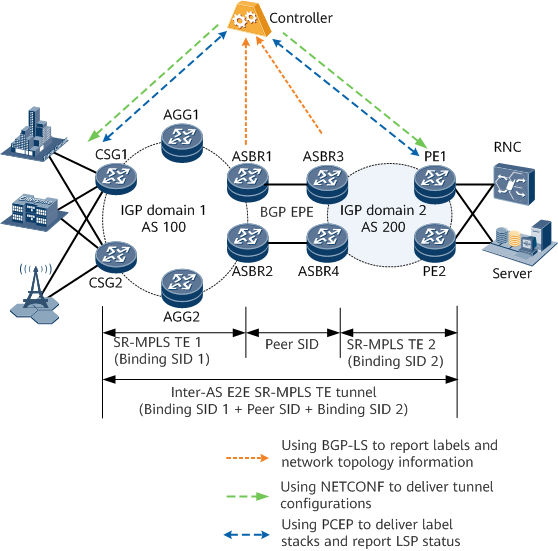
The SR that is extended through an IGP can implement SR-MPLS TE only within an AS domain. To implement inter-AS E2E SR-MPLS TE tunnels, BGP EPE needs to be used to allocate peer SIDs to the adjacencies and nodes between AS domains. Peer SIDs can be advertised to the network controller using BGP-LS. The controller uses the explicit paths to orchestrate IGP SIDs and BGP peer SIDs to implement inter-AS optimal path forwarding on the network shown in Figure 1.
In addition, the label depth supported by an ordinary forwarder is limited, whereas the depth of the label stack of an inter-AS SR-MPLS TE tunnel may exceed the maximum depth supported by a forwarder. To reduce the number of label stack layers encapsulated by the forwarder, use binding SIDs. When configuring an intra-AS SR-MPLS TE tunnel, set a binding SID for the tunnel. The binding SID identifies an SR-MPLS TE tunnel and replaces the label stack of an SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring an inter-AS E2E SR-MPLS TE tunnel, complete the following tasks:
Configure an intra-AS SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
Configure BGP SR between ASBRs.
- Setting a Binding SID
- Using binding SIDs reduces the number of labels in a label stack on an NE, which helps build a large-scale network.
- Configuring an E2E SR-MPLS TE Tunnel Interface
- A tunnel interface must be configured on an ingress so that the interface is used to establish and manage an E2E SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
- (Optional) Configuring SR on a PCC
- The SR capability is configured on a PCC. After a controller calculates a path and delivers path information to a forwarder (PCC), the SR-enabled PCC can establish an SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
- Verifying the Configuration of an Inter-AS E2E SR-MPLS TE Tunnel
- After configuring an inter-AS E2E SR-MPLS TE tunnel, verify information about the SR-MPLS TE tunnel and its status statistics.