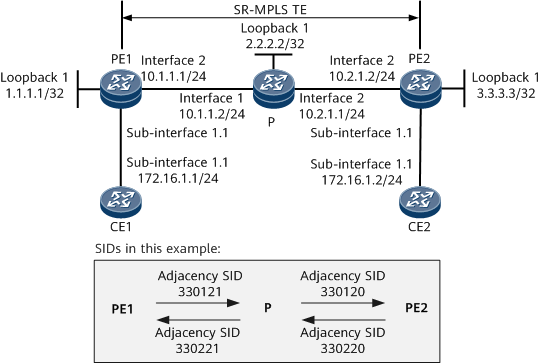
Example for Configuring EVPN VPLS over SR-MPLS TE (Common EVPN Instance)
This section provides an example for configuring an SR-MPLS TE tunnel to carry EVPN VPLS services.
Networking Requirements
To allow different sites to communicate over the backbone network shown in Figure 1, configure EVPN to achieve Layer 2 service transmission. If the sites belong to the same subnet, create an EVPN instance on each PE to store EVPN routes and implement Layer 2 forwarding based on matching MAC addresses. In this example, an SR-MPLS TE tunnel needs to be used to transmit services between the PEs.
Precautions
When configuring EVPN VPLS over SR-MPLS TE, note the following points:
Using the local loopback address of each PE as the source address of the PE is recommended.
- This example uses an explicit path with specified adjacency SIDs to establish the SR-MPLS TE tunnel. Adjacency SIDs that are dynamically generated may change after a device restart, meaning that they need to be reconfigured if adjacency SIDs are specified for the involved explicit path and the involved device is restarted. To facilitate the use of explicit paths, you are advised to run the ipv4 adjacency command to manually configure adjacency SIDs for such paths.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces.
Configure an IGP to enable PE1, PE2, and the P to communicate with each other.
Configure an SR-MPLS TE tunnel on the backbone network.
Configure an EVPN instance on each PE.
Configure an EVPN source address on each PE.
Configure Layer 2 Ethernet sub-interfaces connecting the PEs to CEs.
Configure and apply a tunnel policy to enable EVPN service recursion to the SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
Configure the CEs to communicate with the PEs.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
EVPN instance name: evrf1
RDs (100:1 and 200:1) and RT (1:1) of the EVPN instance evrf1 on PE1 and PE2
Procedure
- Configure IP addresses for interfaces connecting the PEs and the P according to Figure 1.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the P.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P [*HUAWEI] commit [~P] interface loopback 1 [*P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32 [*P-LoopBack1] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.1 24 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P] commit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface loopback 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [*PE2-LoopBack1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure an IGP to enable PE1, PE2, and the P to communicate with each other. IS-IS is used as an example.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.1111.1111.1111.00 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the P.
[~P] isis 1 [*P-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*P-isis-1] network-entity 00.1111.1111.2222.00 [*P-isis-1] quit [*P] interface loopback 1 [*P-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*P-LoopBack1] quit [*P] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.1111.1111.3333.00 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface loopback 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] quit [*PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
After completing the configurations, run the display isis peer command to check whether an IS-IS neighbor relationship has been established between PE1 and the P and between PE2 and the P. If the Up state is displayed in the command output, the neighbor relationship has been successfully established. You can run the display ip routing-table command to check that the PEs have learned the route to each other's loopback 1 interface.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1111.1111.2222 GE0/1/8 1111.1111.2222.01 Up 8s L2 64 Total Peer(s): 1 [~PE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 11 Routes : 11 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 2.2.2.2/32 ISIS-L2 15 10 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 3.3.3.3/32 ISIS-L2 15 20 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.0/24 ISIS-L2 15 20 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
- Configure an SR-MPLS TE tunnel on the backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] mpls te [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] segment-routing [*PE1-segment-routing] quit [*PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] traffic-eng level-2 [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing global-block 153616 153800

The SRGB range varies according to the device. The range specified in this example is for reference only.
[*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis prefix-sid absolute 153700 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] segment-routing [*PE1-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.1.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.1.1.2 sid 330121 [*PE1-segment-routing] quit [*PE1] explicit-path pe1tope2 [*PE1-explicit-path-pe1tope2] next sid label 330121 type adjacency [*PE1-explicit-path-pe1tope2] next sid label 330120 type adjacency [*PE1-explicit-path-pe1tope2] quit [*PE1] interface tunnel1 [*PE1-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1 [*PE1-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*PE1-Tunnel1] destination 3.3.3.3 [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te tunnel-id 1 [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te signal-protocol segment-routing [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te path explicit-path pe1tope2 [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te reserved-for-binding [*PE1-Tunnel1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the P.
[~P] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*P] mpls [*P-mpls] mpls te [*P-mpls] quit [*P] segment-routing [*P-segment-routing] quit [*P] isis 1 [*P-isis-1] cost-style wide [*P-isis-1] traffic-eng level-2 [*P-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*P-isis-1] segment-routing global-block 153616 153800

The SRGB range varies according to the device. The range specified in this example is for reference only.
[*P-isis-1] quit [*P] interface loopback 1 [*P-LoopBack1] isis prefix-sid absolute 153710 [*P-LoopBack1] quit [*P] segment-routing [*P-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.1.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.1.1.1 sid 330221 [*P-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.2.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.2.1.2 sid 330120 [*P-segment-routing] quit [*P] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] mpls te [*PE2-mpls] quit [*PE2] segment-routing [*PE2-segment-routing] quit [*PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE2-isis-1] traffic-eng level-2 [*PE2-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*PE2-isis-1] segment-routing global-block 153616 153800

The SRGB range varies according to the device. The range specified in this example is for reference only.
[*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface loopback 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis prefix-sid absolute 153720 [*PE2-LoopBack1] quit [*PE2] segment-routing [*PE2-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.2.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.2.1.1 sid 330220 [*PE2-segment-routing] quit [*PE2] explicit-path pe2tope1 [*PE2-explicit-path-pe2tope1] next sid label 330220 type adjacency [*PE2-explicit-path-pe2tope1] next sid label 330221 type adjacency [*PE2-explicit-path-pe2tope1] quit [*PE2] interface tunnel1 [*PE2-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1 [*PE2-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*PE2-Tunnel1] destination 1.1.1.1 [*PE2-Tunnel1] mpls te tunnel-id 1 [*PE2-Tunnel1] mpls te signal-protocol segment-routing [*PE2-Tunnel1] mpls te path explicit-path pe2tope1 [*PE2-Tunnel1] mpls te reserved-for-binding [*PE2-Tunnel1] quit [*PE2] commit
After completing the configurations, run the display mpls te tunnel-interface command. The command output shows that the tunnel state is up.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display mpls te tunnel-interface Tunnel Name : Tunnel1 Signalled Tunnel Name: - Tunnel State Desc : CR-LSP is Up Tunnel Attributes : Active LSP : Primary LSP Traffic Switch : - Session ID : 1 Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID: 3.3.3.3 Admin State : UP Oper State : UP Signaling Protocol : Segment-Routing FTid : 1 Tie-Breaking Policy : None Metric Type : None Bfd Cap : None Reopt : Disabled Reopt Freq : - Auto BW : Disabled Threshold : - Current Collected BW: - Auto BW Freq : - Min BW : - Max BW : - Offload : Disabled Offload Freq : - Low Value : - High Value : - Readjust Value : - Offload Explicit Path Name: - Tunnel Group : Primary Interfaces Protected: - Excluded IP Address : - Referred LSP Count : 0 Primary Tunnel : - Pri Tunn Sum : - Backup Tunnel : - Group Status : Up Oam Status : None IPTN InLabel : - Tunnel BFD Status : - BackUp LSP Type : None BestEffort : - Secondary HopLimit : - BestEffort HopLimit : - Secondary Explicit Path Name: - Secondary Affinity Prop/Mask: 0x0/0x0 BestEffort Affinity Prop/Mask: - IsConfigLspConstraint: - Hot-Standby Revertive Mode: Revertive Hot-Standby Overlap-path: Disabled Hot-Standby Switch State: CLEAR Bit Error Detection: Disabled Bit Error Detection Switch Threshold: - Bit Error Detection Resume Threshold: - Ip-Prefix Name : - P2p-Template Name : - PCE Delegate : No LSP Control Status : Local control Path Verification : No Entropy Label : - Associated Tunnel Group ID: - Associated Tunnel Group Type: - Auto BW Remain Time : - Reopt Remain Time : - Segment-Routing Remote Label : - Binding Sid : - Reverse Binding Sid : - FRR Attr Source : - Is FRR degrade down : - Primary LSP ID : 1.1.1.1:1 LSP State : UP LSP Type : Primary Setup Priority : 7 Hold Priority: 7 IncludeAll : 0x0 IncludeAny : 0x0 ExcludeAny : 0x0 Affinity Prop/Mask : 0x0/0x0 Resv Style : SE Configured Bandwidth Information: CT0 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT1 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT2 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT3 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT4 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT5 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT6 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT7 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 Actual Bandwidth Information: CT0 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT1 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT2 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT3 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT4 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT5 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT6 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 CT7 Bandwidth(Kbit/sec): 0 Explicit Path Name : pe1tope2 Hop Limit: - Record Route : - Record Label : - Route Pinning : - FRR Flag : - IdleTime Remain : - BFD Status : - Soft Preemption : - Reroute Flag : - Pce Flag : Normal Path Setup Type : EXPLICIT Create Modify LSP Reason: - - Configure an EVPN instance on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE1-evpn-instance-evrf1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-evpn-instance-evrf1] vpn-target 1:1 [*PE1-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE2-evpn-instance-evrf1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE2-evpn-instance-evrf1] vpn-target 1:1 [*PE2-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure an EVPN source address on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] evpn source-address 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] evpn source-address 3.3.3.3 [*PE2] commit
- Configure Layer 2 Ethernet sub-interfaces connecting the PEs to the CEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1] evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*PE2-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1] evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure and apply a tunnel policy to enable EVPN service recursion to the SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] tunnel-policy srte [*PE1-tunnel-policy-srte] tunnel binding destination 3.3.3.3 te Tunnel1 [*PE1-tunnel-policy-srte] quit [*PE1] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE1-evpn-instance-evrf1] tnl-policy srte [*PE1-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] tunnel-policy srte [*PE2-tunnel-policy-srte] tunnel binding destination 1.1.1.1 te Tunnel1 [*PE2-tunnel-policy-srte] quit [*PE2] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE2-evpn-instance-evrf1] tnl-policy srte [*PE2-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
After completing the configurations, run the display bgp evpn peer command to check whether the BGP peer relationship has been established between the PEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationship has been successfully established. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn peer BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.3 4 100 43 44 0 00:34:03 Established 1 - Configure the CEs to communicate with the PEs.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] ip address 172.16.1.1 24 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0.1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] ip address 172.16.1.2 24 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*CE2] commit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table command on each PE. The command output shows EVPN routes sent from the remote PE. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table Local AS number : 100 BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete EVPN address family: Number of Mac Routes: 2 Route Distinguisher: 100:1 Network(EthTagId/MacAddrLen/MacAddr/IpAddrLen/IpAddr) NextHop *> 0:48:00e0-fc21-0302:0:0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Route Distinguisher: 200:1 Network(EthTagId/MacAddrLen/MacAddr/IpAddrLen/IpAddr) NextHop *>i 0:48:00e0-fc61-0300:0:0.0.0.0 3.3.3.3 EVPN-Instance evrf1: Number of Mac Routes: 2 Network(EthTagId/MacAddrLen/MacAddr/IpAddrLen/IpAddr) NextHop *> 0:48:00e0-fc21-0302:0:0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 *>i 0:48:00e0-fc61-0300:0:0.0.0.0 3.3.3.3 EVPN address family: Number of Inclusive Multicast Routes: 2 Route Distinguisher: 100:1 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *> 0:32:1.1.1.1 127.0.0.1 Route Distinguisher: 200:1 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *>i 0:32:3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 EVPN-Instance evrf1: Number of Inclusive Multicast Routes: 2 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *> 0:32:1.1.1.1 127.0.0.1 *>i 0:32:3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table mac-route 0:48:00e0-fc61-0300:0:0.0.0.0 command on PE1 to check details about the specified MAC route. The command output shows the name of the tunnel interface to which the route recurses.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table mac-route 0:48:00e0-fc61-0300:0:0.0.0.0 BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total routes of Route Distinguisher(200:1): 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0:48:00e0-fc61-0300:0:0.0.0.0: Label information (Received/Applied): 48122/NULL From: 3.3.3.3 (10.2.1.2) Route Duration: 0d00h01m40s Relay IP Nexthop: 10.1.1.2 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Original nexthop: 3.3.3.3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1> AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255, IGP cost 20 Route Type: 2 (MAC Advertisement Route) Ethernet Tag ID: 0, MAC Address/Len: 00e0-fc61-0300/48, IP Address/Len: 0.0.0.0/0, ESI:0000.0000.0000.0000.0000 Not advertised to any peer yet EVPN-Instance evrf1: Number of Mac Routes: 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0:48:00e0-fc61-0300:0:0.0.0.0: Route Distinguisher: 200:1 Remote-Cross route Label information (Received/Applied): 48122/NULL From: 3.3.3.3 (10.2.1.2) Route Duration: 0d00h01m40s Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: Tunnel1 Original nexthop: 3.3.3.3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1> AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255 Route Type: 2 (MAC Advertisement Route) Ethernet Tag ID: 0, MAC Address/Len: 00e0-fc61-0300/48, IP Address/Len: 0.0.0.0/0, ESI:0000.0000.0000.0000.0000 Not advertised to any peer yet
Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table inclusive-route 0:32:3.3.3.3 command on PE1 to check details about the specified inclusive multicast route. The command output shows the name of the tunnel interface to which the route recurses.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table inclusive-route 0:32:3.3.3.3 BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total routes of Route Distinguisher(200:1): 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0:32:3.3.3.3: Label information (Received/Applied): 48123/NULL From: 3.3.3.3 (10.2.1.2) Route Duration: 0d00h04m49s Relay IP Nexthop: 10.1.1.2 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Original nexthop: 3.3.3.3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1> AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255, IGP cost 20 PMSI: Flags 0, Ingress Replication, Label 0:0:0(48123), Tunnel Identifier:3.3.3.3 Route Type: 3 (Inclusive Multicast Route) Ethernet Tag ID: 0, Originator IP:3.3.3.3/32 Not advertised to any peer yet EVPN-Instance evrf1: Number of Inclusive Multicast Routes: 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0:32:3.3.3.3: Route Distinguisher: 200:1 Remote-Cross route Label information (Received/Applied): 48123/NULL From: 3.3.3.3 (10.2.1.2) Route Duration: 0d00h04m45s Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: Tunnel1 Original nexthop: 3.3.3.3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1> AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255 PMSI: Flags 0, Ingress Replication, Label 0:0:0(48123), Tunnel Identifier:3.3.3.3 Route Type: 3 (Inclusive Multicast Route) Ethernet Tag ID: 0, Originator IP:3.3.3.3/32 Not advertised to any peer yet
Run the ping command on the CEs. The command output shows that the CEs belonging to the same VPN instance can ping each other. For example:
[~CE1] ping 172.16.1.2 PING 172.16.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=11 ms Reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=9 ms Reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=4 ms Reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=6 ms Reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=7 ms --- 172.16.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 4/7/11 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # evpn vpn-instance evrf1 route-distinguisher 100:1 tnl-policy srte vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls mpls te # explicit-path pe1tope2 next sid label 330121 type adjacency next sid label 330120 type adjacency # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.1.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.1.1.2 sid 330121 # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 00.1111.1111.1111.00 traffic-eng level-2 segment-routing mpls segment-routing global-block 153616 153800 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 vlan-type dot1q 10 evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 isis prefix-sid absolute 153700 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol segment-routing mpls te reserved-for-binding mpls te tunnel-id 1 mpls te path explicit-path pe1tope2 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.3 enable # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # tunnel-policy srte tunnel binding destination 3.3.3.3 te Tunnel1 # evpn source-address 1.1.1.1 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls mpls te # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.1.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.1.1.1 sid 330221 ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.2.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.2.1.2 sid 330120 # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 00.1111.1111.2222.00 traffic-eng level-2 segment-routing mpls segment-routing global-block 153616 153800 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 isis prefix-sid absolute 153710 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # evpn vpn-instance evrf1 route-distinguisher 200:1 tnl-policy srte vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls mpls te # explicit-path pe2tope1 next sid label 330220 type adjacency next sid label 330221 type adjacency # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.2.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.2.1.1 sid 330220 # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 00.1111.1111.3333.00 traffic-eng level-2 segment-routing mpls segment-routing global-block 153616 153800 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 vlan-type dot1q 10 evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 isis prefix-sid absolute 153720 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.1 mpls te signal-protocol segment-routing mpls te reserved-for-binding mpls te tunnel-id 1 mpls te path explicit-path pe2tope1 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # tunnel-policy srte tunnel binding destination 1.1.1.1 te Tunnel1 # evpn source-address 3.3.3.3 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 vlan-type dot1q 10 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 vlan-type dot1q 10 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # return