IS-IS for SRv6
Name |
Function |
Carried In |
|---|---|---|
SRv6 Locator TLV |
Advertises an SRv6 locator and the End SIDs associated with it. |
IS-IS LSP |
SRv6 Capabilities sub-TLV |
Advertises SRv6 capabilities. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
SRv6 End SID sub-TLV |
Advertises SRv6 SIDs. |
SRv6 Locator TLV |
SRv6 End.X SID sub-TLV |
Advertises SRv6 SIDs on a point-to-point (P2P) network. |
|
SRv6 LAN End.X SID sub-TLV |
Advertises SRv6 SIDs on a local area network (LAN). |
|
Node MSD sub-TLV |
Advertises the maximum SID depth (MSD) supported by a device. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
IS-IS FAD sub-TLV |
Advertises the Flex-Algo definition (FAD) of IS-IS. For details, see SRv6 Flex-Algo. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
SR-Algorithm sub-TLV |
Advertises the algorithm that is used. For details, see SRv6 Flex-Algo. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
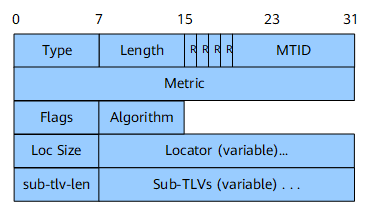
SRv6 Locator TLV
The SRv6 Locator TLV is used to advertise an SRv6 locator and the End SIDs associated with it. Figure 1 shows its format.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Type. |
Length |
8 bits |
Length. |
MTID |
12 bits |
Multi-topology identifier. |
Metric |
32 bits |
Metric. |
Flags |
8 bits |
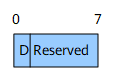
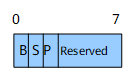
Flags bit, expressed using the format shown in Figure 2. Currently, only the D bit is available. When a SID is leaked from Level-2 to Level-1, the D bit must be set. SIDs with the D bit set must not be leaked from Level-1 to Level-2 to prevent route loops.
|
Algorithm |
8 bits |
Associated algorithm:
|
Loc Size |
8 bits |
Number of bits in the Locator field. |
Locator (variable) |
Variable length |
Advertised SRv6 locator. |
sub-tlv-len |
8 bits |
Sub-TLV length. |
Sub-TLVs (variable) |
Variable length |
Included sub-TLVs, for example, SRv6 End SID sub-TLV. |
SRv6 locators can be advertised using the SRv6 Locator TLV. After receiving the TLV, SRv6-capable IS-IS devices install corresponding locator route entries to their local forwarding tables, but SRv6-incapable IS-IS devices do not.
SRv6 locators can also be advertised using the Prefix Reachability TLV 236 or 237. In this advertisement mode, SRv6-incapable devices can install corresponding locator route entries to their local forwarding tables, thereby achieving interworking with SRv6-capable devices. In cases where a locator advertisement is received in both a Prefix Reachability TLV and an SRv6 Locator TLV, the Prefix Reachability TLV is preferentially used.
SRv6 Capabilities Sub-TLV
In SRv6, segment list information is stored in the Segment Routing header (SRH). SRv6-capable nodes must be able to process SRH information under certain restrictions. The SRv6 Capabilities sub-TLV is used to advertise the SRv6 capabilities supported by the local node. Figure 3 shows its format.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Type. |
Length |
8 bits |
Length. |
Flags |
16 bits |
Flag bit. |
Optional sub-sub-TLVs |
Variable length |
Optional sub-sub-TLVs. |
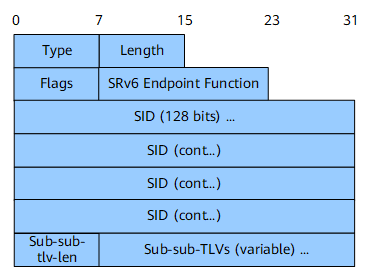
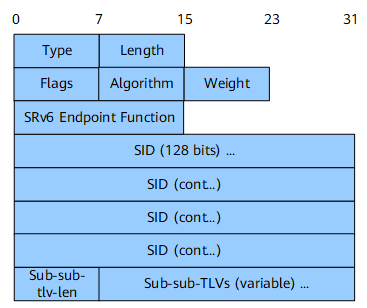
SRv6 End SID Sub-TLV
The SRv6 End SID sub-TLV is used to advertise SRv6 End SIDs with endpoint functions. Figure 4 shows its format.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Type. |
Length |
8 bits |
Length. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flag bit. |
SRv6 Endpoint Function |
16 bits |
SRv6 endpoint function. For details about supported values, see SRv6 Endpoint Function. |
SID |
16 octets |
Advertised SRv6 SID. |
Sub-sub-tlv-len |
8 bits |
Sub-sub-TLV length. |
Sub-sub-TLVs (variable) |
Variable length |
Included sub-sub-TLVs. |
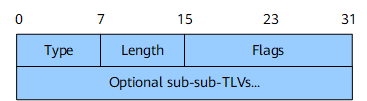
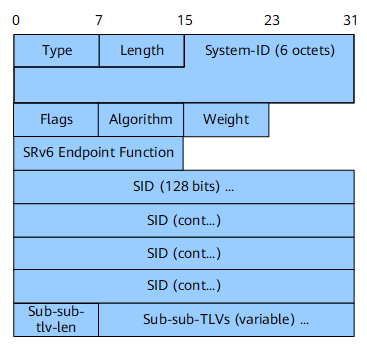
SRv6 End.X SID Sub-TLV
The SRv6 End.X SID sub-TLV is used to advertise an SRv6 End.X SID associated with a P2P adjacency. Figure 5 shows its format.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Type. |
Length |
8 bits |
Length. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flag bit. Figure 6 shows the format of this field.
|
Algorithm |
8 bits |
Associated algorithm. |
Weight |
8 bits |
Weight of the End.X SID for the purpose of load balancing. |
SRv6 Endpoint Function |
16 bits |
SRv6 endpoint function. For details about supported values, see SRv6 Endpoint Function. |
SID |
16 octets |
Advertised SRv6 SID. |
Sub-sub-tlv-len |
8 bits |
Sub-sub-TLV length. |
Sub-sub-TLVs (variable) |
Variable length |
Included sub-sub-TLVs. |
SRv6 LAN End.X SID Sub-TLV
The SRv6 LAN End.X SID sub-TLV is used to advertise an SRv6 End.X SID associated with a LAN adjacency. Figure 7 shows its format.
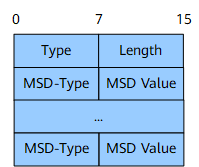
Node MSD Sub-TLV
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Type. |
Length |
8 bits |
Length. |
MSD-Type |
8 bits |
MSD type:
|
MSD Value |
8 bits |
MSD value. |
SRv6 Endpoint Function
SRv6 uses endpoint functions to define the behaviors associated with different SIDs. In addition to advertising locator routes, IS-IS advertises SRv6 SIDs and their associated SRv6 endpoint functions through various SID sub-TLVs for path/service programming units to perform network programming. Table 8 shows the SRv6 endpoint functions that can be advertised by IS-IS. In this table, "Y" indicates that the corresponding sub-TLV can advertise the specified type of SRv6 endpoint function, and "N" indicates that the corresponding sub-TLV cannot advertise the specified type of SRv6 endpoint function.
SRv6 Endpoint Function |
SRv6 End SID Sub-TLV |
SRv6 End.X SID Sub-TLV |
SRv6 LAN End.X SID Sub-TLV |
|---|---|---|---|
End (no PSP, no USP) |
Y |
N |
N |
End (with PSP) |
Y |
N |
N |
End (with USP) |
Y |
N |
N |
End (with PSP & USP) |
Y |
N |
N |
End.X (no PSP, no USP) |
N |
Y |
Y |
End.X (with PSP) |
N |
Y |
Y |
End.X (with USP) |
N |
Y |
Y |
End.X (with PSP & USP) |
N |
Y |
Y |
End.DT4 |
Y |
N |
N |
End.DT6 |
Y |
N |
N |
End.DX4 |
N |
Y |
Y |
End.DX6 |
N |
Y |
Y |
End.OP |
Y |
N |
N |