SRv6 TE Policy Creation
An SRv6 TE Policy can be manually configured on a forwarder through CLI or NETCONF. Alternatively, it can be delivered to a forwarder after being dynamically generated by a protocol, such as BGP, on a controller. The dynamic mode facilitates network deployment. If the same SRv6 TE Policies generated in both modes exist, the forwarder selects an SRv6 TE Policy based on the same rules adopted for SR-MPLS TE Policy selection. For details, see SR-MPLS TE Policy Creation.
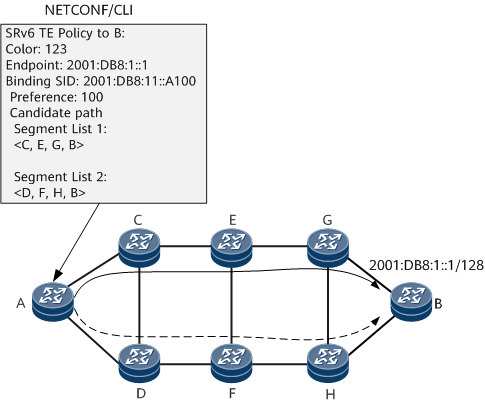
An SRv6 TE Policy can be created using End SIDs, End.X SIDs, anycast SIDs, binding SIDs, or a combination of them.
Figure 1 shows an example of manually configuring an SRv6 TE Policy through CLI or NETCONF. For a manually configured SRv6 TE Policy, information, such as the endpoint and color attributes, the preference values of candidate paths, and segment lists, must be configured. In addition, the preference values of candidate paths in the same SRv6 TE Policy cannot be the same.
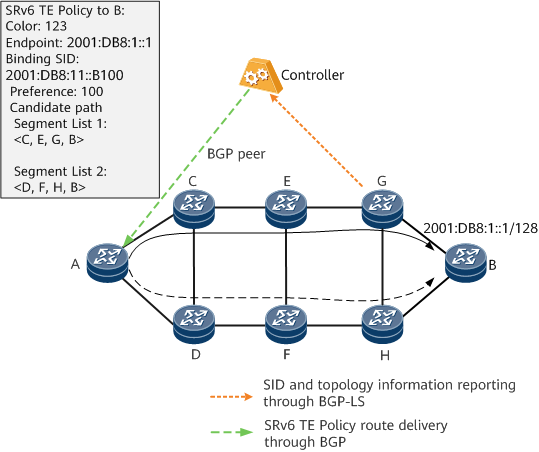
Figure 2 shows the process in which a controller dynamically generates and delivers an SRv6 TE Policy to a forwarder. The process is as follows:
The controller collects information, such as network topology and SID information, through BGP-LS. Network topology information includes link cost, latency, packet loss rate and more.
The controller and headend forwarder establish a BGP peer relationship in the BGP IPv6 SR-Policy address family.
The controller computes an SRv6 TE Policy based on link cost, latency, packet loss rate and other factors, and then delivers the SRv6 TE Policy to the headend through a BGP peer relationship. The headend forwarder then generates SRv6 TE Policy entries.
For a manually configured SRv6 TE Policy, a binding SID is configured within the static segment of the corresponding locator.
The controller supports the following SRv6 TE Policy delivery modes:
- Manually deploy an SRv6 TE Policy and configure a binding SID within the static segment of the corresponding locator. Then, use the controller to deliver a candidate path of the SRv6 TE Policy and select the configured binding SID as the binding SID of the SRv6 TE Policy.
- Use the controller to directly deliver an SRv6 TE Policy that either carries a binding SID within the dynamic segment of the corresponding locator or does not carry any binding SID. (In the latter case, the forwarder receiving the policy randomly allocates a binding SID within the dynamic segment of the corresponding locator.)
After receiving the SRv6 TE Policy, the forwarder reports the SRv6 TE Policy status information containing the effective binding SID to the controller through BGP-LS. This allows the controller to obtain the binding SID of the SRv6 TE Policy, and then use the binding SID for SRv6 path orchestration.