Comparison of Network Slicing Solutions
Characteristics of the Slice ID-based Network Slicing Solution
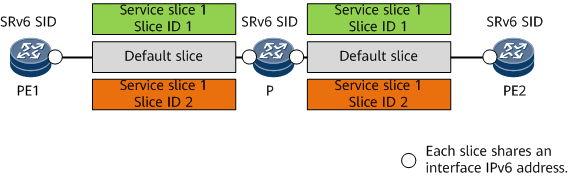
Slice ID-based network slicing enables a basic physical network to be shared and forwarding resources to be logically sliced. Service slices and the default slice (physical network) have resource differences only on the forwarding plane and share the control plane.
As shown in Figure 1, in this solution, IPv6 addresses do not need to be repeatedly configured for service slices. Instead, information such as the IPv6 address, cost, and End/End.X SID of the default slice is directly inherited. An SRv6 TE Policy is configured on a basic physical network. Slice IDs of the SRv6 TE Policy are used to invoke different forwarding resources of network slicing.
Characteristics of the Affinity-based Network Slicing Solution
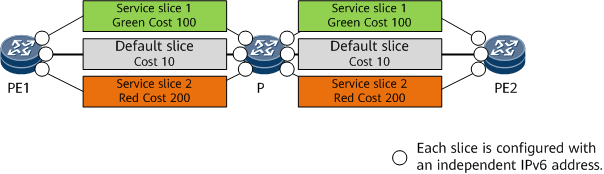
Affinity-based network slicing allows a physical network to be sliced. Service slices and the default slice (physical network) are separated and independent on the control plane.
In this solution, service slices have independent links, IPv6 addresses need to be repeatedly configured, routing protocols independently run, and SIDs are independently allocated. SRv6 TE Policies are independently configured for different service slices. Services are diverted to the corresponding slices through different SRv6 TE Policies.