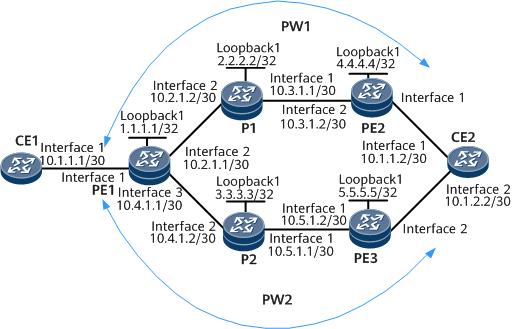
Example for Configuring BFD for VPWS PW
Using BFD to detect PW faults involves simple configurations and requires a few packet exchanges.
Networking Requirements
On the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 2 virtual private network (L2VPN):
PW1 is established between PE1 and PE2 and serves as the primary PW.
PW2 is established between PE1 and PE3 and serves as the secondary PW.
On the network shown in Figure 1, BFD needs to be configured to monitor the connectivity of the primary and secondary PWs, so that services can switch to the secondary PW within 50 ms if the primary PW fails.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure MPLS capabilities.
Establish PW1 between PE1 and PE2 and PW2 between PE1 and PE3. Configure PW1 as the primary PW and PW2 as the secondary PW on AC interfaces of PE1.
Configure BFD to monitor the connectivity of PW1 and PW2.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP addresses of interfaces
VC IDs of PWs
Names and the local and remote discriminators of BFD sessions
Procedure
- Assign IP addresses to CE interfaces that connect to PEs.
# Configure CE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*CE1] commit [~CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.1 30 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.2.1 30 sub [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure CE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE2 [*CE2] commit [~CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.2 30 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.1.2.2 30 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Configure an IGP (OSPF is used as an example) on the MPLS backbone network so that PEs and Ps can communicate.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.2.1.1 30 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 10.4.1.1 30 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE1] commit [~PE1] ospf 1 [*PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] interface loopback 1 [*P1-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32 [*P1-LoopBack1] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.3.1.1 30 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.2.1.2 30 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*P1] commit [~P1] ospf 1 [*P1-ospf-1] area 0 [*P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 [*P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] interface loopback 1 [*P2-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [*P2-LoopBack1] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.5.1.1 30 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.4.1.2 30 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*P2] commit [~P2] ospf 1 [*P2-ospf-1] area 0 [*P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 [*P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*P2] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface loopback 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32 [*PE2-LoopBack1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.3.1.2 30 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE2] commit [~PE2] ospf 1 [*PE2-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
[*PE3] interface loopback 1 [*PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32 [*PE3-LoopBack1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.5.1.2 30 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE3] commit [~PE3] ospf 1 [*PE3-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.3 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE3] commit
After completing the configurations, run the display ip routing-table command on each PE. The command output shows that PE1 and PE2 have learned the routes to each other's Loopback1 interface, and PE1 and PE3 have learned the routes to each other's Loopback1 interface.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 15 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 2.2.2.2/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 3.3.3.3/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 4.4.4.4/32 OSPF 10 3 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 5.5.5.5/32 OSPF 10 3 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 10.2.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.2.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 10.2.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 10.2.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 10.3.1.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 10.4.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.4.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 10.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 10.4.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 10.5.1.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.4.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2
- Configure basic MPLS functions on the MPLS backbone network.
# Enable MPLS and configure the Loopback1 address as an LSR ID on each involved device. Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP on involved interfaces connected to the MPLS backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*P1] mpls [*P1-mpls] quit [*P1] mpls ldp [*P1-mpls-ldp] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*P2] mpls [*P2-mpls] quit [*P2] mpls ldp [*P2-mpls-ldp] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] quit [*PE2] mpls ldp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 [*PE3] mpls [*PE3-mpls] quit [*PE3] mpls ldp [*PE3-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display tunnel-info all command each PE. The command output shows that an MPLS LSP has been established between PE1 and PE2 and between PE1 and PE3.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display tunnel-info all Tunnel ID Type Destination Status ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 0x000000000300000000 ldp 2.2.2.2 UP 0x000000000300000001 ldp -- UP 0x000000000300000002 ldp 3.3.3.3 UP 0x000000000300000003 ldp -- UP 0x000000000300000004 ldp 4.4.4.4 UP 0x000000000300000005 ldp -- UP 0x000000000300000006 ldp 5.5.5.5 UP 0x000000000300000007 ldp -- UP
Run the display mpls ldp session command on each PE. The command output shows that the Status field is Operational, indicating that an LDP peer relationship has been established between this PE and its neighboring P.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) An asterisk (*) before a session means the session is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2.2.2.2:0 Operational DU Passive 000:00:03 16/16 3.3.3.3:0 Operational DU Passive 000:00:03 13/13 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 2 session(s) Found. - Establish a remote LDP session between PE1 and PE2.
# Configure a remote LDP session, and use the loopback interface address of a remote LDP peer as the remote peer address.

If two PEs are directly connected, you do not need to configure a remote LDP session between them.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp remote-peer 4.4.4.4 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-4.4.4.4] remote-ip 4.4.4.4 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-4.4.4.4] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp remote-peer 5.5.5.5 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-5.5.5.5] remote-ip 5.5.5.5 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-5.5.5.5] commit [~PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-5.5.5.5] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls ldp remote-peer 1.1.1.1 [*PE2-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.1] remote-ip 1.1.1.1 [*PE2-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.1] commit [~PE2-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.1] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] mpls ldp remote-peer 1.1.1.1 [*PE3-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.1] remote-ip 1.1.1.1 [*PE3-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.1] commit [~PE3-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.1] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display mpls ldp session command on each PE. The command output shows that the Status field is Operational, indicating that a remote LDP peer relationship has been established.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) An asterisk (*) before a session means the session is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2.2.2.2:0 Operational DU Passive 000:00:06 27/27 3.3.3.3:0 Operational DU Passive 000:00:05 24/24 4.4.4.4:0 Operational DU Passive 000:00:00 3/3 5.5.5.5:0 Operational DU Passive 000:00:00 2/2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 4 session(s) Found. - Configure PWs on PEs using PW templates.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls l2vpn [*PE1-l2vpn] quit [*PE1] pw-template 1to2 [*PE1-pw-template-1to2] peer-address 4.4.4.4 [*PE1-pw-template-1to2] control-word [*PE1-pw-template-1to2] quit [*PE1] pw-template 1to3 [*PE1-pw-template-1to3] peer-address 5.5.5.5 [*PE1-pw-template-1to3] control-word [*PE1-pw-template-1to3] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls l2vc pw-template 1to2 100 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls l2vc pw-template 1to3 200 secondary [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls l2vpn [*PE2-l2vpn] quit [*PE2] pw-template 2to1 [*PE2-pw-template-2to1] peer 1.1.1.1 [*PE2-pw-template-2to1] control-word [*PE2-pw-template-2to1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls l2vc pw-template 2to1 100 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] mpls l2vpn [*PE3-l2vpn] quit [*PE3] pw-template 3to1 [*PE3-pw-template-3to1] peer 1.1.1.1 [*PE3-pw-template-3to1] control-word [*PE3-pw-template-3to1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls l2vc pw-template 3to1 200 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display pw-template command on each PE. The command output shows PW template configurations.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display pw-template Total PW template number : 2 PW Template Name : 1to2 PeerIP : 4.4.4.4 Tnl Policy Name : -- CtrlWord : Enable MTU : 1500 Seq-Number : Disable TDM Encapsulation Number: 32 Jitter-Buffer : 20 Jitter-Buffer-Cep : 1125 Payload-Compression DBA : UNEQ Idle-Code : ff Rtp-Header : Disable VCCV Capability : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Behavior Name : -- Total PW : 1, Static PW : 0, LDP PW : 1 PW Template Name : 1to3 PeerIP : 5.5.5.5 Tnl Policy Name : -- CtrlWord : Enable MTU : 1500 Seq-Number : Disable TDM Encapsulation Number: 32 Jitter-Buffer : 20 Jitter-Buffer-Cep : 1125 Payload-Compression DBA : UNEQ Idle-Code : ff Rtp-Header : Disable VCCV Capability : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Behavior Name : -- Total PW : 1, Static PW : 0, LDP PW : 1
After completing the configurations, run the display mpls l2vc interface command on each PE. The command output shows that PWs have been established and are in the Active state, and that BFD for PW is not configured for the primary and secondary PWs.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display mpls l2vc interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 *client interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 is up session state : up AC status : up VC state : up VC ID : 100 VC type : PPP destination : 4.4.4.4 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 21504 remote VC label : 21504 local AC OAM State : up local PSN State : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote statuscode : 0x0 BFD for PW : unavailable manual fault : not set active state : active forwarding entry : exist link state : up local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 Local VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Remote VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy name : -- traffic behavior name : -- PW template name : 1to2 primary or secondary : primary VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x1002004 create time : 0 days, 1 hours, 22 minutes, 22 seconds up time : 0 days, 1 hours, 21 minutes, 14 seconds last change time : 0 days, 1 hours, 21 minutes, 14 seconds VC last up time : 2008-07-24 12:31:31 VC total up time: 0 days, 2 hours, 12 minutes, 51 seconds CKey : 16 NKey : 15 *client interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 is up session state : up AC status : up VC state : up VC ID : 200 VC type : PPP destination : 5.5.5.5 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 21505 remote VC label : 21504 local AC OAM state : up local PSN state : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote statuscode : 0x0 BFD for PW : unavailable manual fault : not set active state : inactive forwarding entry : existent link state : up local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 Local VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Remote VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy : -- traffic behavior : -- PW template name : 1to3 primary or secondary : secondary VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x1002006 create time : 0 days, 1 hours, 22 minutes, 9 seconds up time : 0 days, 1 hours, 20 minutes, 22 seconds last change time : 0 days, 1 hours, 20 minutes, 22 seconds VC last up time : 2008-07-24 12:31:31 VC total up time: 0 days, 2 hours, 12 minutes, 51 seconds CKey : 17 NKey : 18 reroute policy : delay 30 s, resume 10 s reason of last reroute : -- time of last reroute : -- days, -- hours, -- minutes, -- seconds delay timer ID : -- residual time :-- resume timer ID : -- residual time :--
- Configure BFD for VPWS PW on PEs.
Currently, static BFD and dynamic BFD are supported. For the same VPWS PW, the static BFD session and dynamic BFD session are mutually exclusive. That is, only a single type of BFD session can be configured.

In this example, the configuration static BFD for VPWS PW is displayed in the configuration file.
- Configure static BFD.

For a BFD session, the local discriminator on one end must be the same as the remote discriminator on the other end.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bfd [*PE1-bfd] quit [*PE1] bfd 1to2 bind pw interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to2] discriminator local 12 [*PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to2] discriminator remote 21 [*PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to2] commit [~PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to2] quit [*PE1] bfd 1to3 bind pw interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 secondary [*PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to3] discriminator local 13 [*PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to3] discriminator remote 31 [*PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to3] commit [~PE1-bfd-lsp-session-1to3] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bfd [*PE2-bfd] quit [*PE2] bfd 2to1 bind pw interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-bfd-lsp-session-2to1] discriminator local 21 [*PE2-bfd-lsp-session-2to1] discriminator remote 12 [*PE2-bfd-lsp-session-2to1] commit [~PE2-bfd-lsp-session-2to1] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bfd [*PE3-bfd] quit [*PE3] bfd 3to1 bind pw interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE3-bfd-lsp-session-3to1] discriminator local 31 [*PE3-bfd-lsp-session-3to1] discriminator remote 13 [*PE3-bfd-lsp-session-3to1] commit [~PE3-bfd-lsp-session-3to1] quit
After the configuration is complete, BFD sessions can be created between PE1 and PE2, and between PE1 and PE3. Run the display bfd session all command. The command output shows that the BFD state field is up.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display bfd session all (w): State in WTR (*): State is invalid -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Local Remote PeerIpAddr State Type InterfaceName -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12 21 --.--.--.-- Up S_PW(M) GigabitEthernet0/1/0 13 31 --.--.--.-- Up S_PW(S) GigabitEthernet0/1/0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total UP/DOWN Session Number : 2/0
- Configure dynamic BFD.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bfd [*PE1-bfd] quit [*PE1] pw-template 1to2 [*PE1-pw-template-1to2] control-word [*PE1-pw-template-1to2] bfd-detect min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 [*PE1-pw-template-1to2] quit [*PE1] pw-template 1to3 [*PE1-pw-template-1to3] control-word [*PE1-pw-template-1to3] bfd-detect min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 [*PE1-pw-template-1to3] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 secondary [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bfd [*PE2-bfd] quit [*PE2] pw-template 2to1 [*PE2-pw-template-2to1] control-word [*PE2-pw-template-2to1] bfd-detect min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 [*PE2-pw-template-2to1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 track-interface [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bfd [*PE3-bfd] quit [*PE3] pw-template 3to1 [*PE3-pw-template-3to1] control-word [*PE3-pw-template-3to1] bfd-detect min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 [*PE3-pw-template-3to1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 detect-multiplier 4 track-interface [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
After the configuration is complete, BFD sessions can be created between PE1 and PE2, and between PE1 and PE3. Run the display bfd session all command. The command output shows that the BFD state field is up.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display bfd session all (w): State in WTR (*): State is invalid -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Local Remote PeerIpAddr State Type InterfaceName -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12 21 --.--.--.-- Up D_PW(M) GigabitEthernet0/1/0 13 31 --.--.--.-- Up D_PW(S) GigabitEthernet0/1/0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total UP/DOWN Session Number : 2/0
- Configure static BFD.
- Verify the configuration.

Verify the configuration of static BFD for VPWS PW. The procedure for verifying dynamic BFD for VPWS PW is similar to that for verifying static BFD for VPWS PW.
When the primary PW is working properly, CE1 can use the primary address to ping CE2's 10.1.1.2. Because the secondary PW does not work, CE1 cannot use the secondary address to ping CE2's 10.1.2.2.
<CE1> ping 10.1.1.2 PING 10.1.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=140 ms Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=90 ms Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=120 ms Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=120 ms Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=130 ms --- 10.1.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 90/120/140 ms <CE1> ping 10.1.2.2 PING 10.1.2.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Request time out Request time out Request time out Request time out Request time out --- 10.1.2.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 0 packet(s) received 100.00% packet loss# Run the display mpls l2vc interface command on each PE. The command output shows that the BFD for PW field is available, and the BFD state field is up for both the primary and secondary PWs.
<PE1> display mpls l2vc interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 *client interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 is up session state : up AC status : up VC state : up VC ID : 100 VC type : Ethernet destination : 4.4.4.4 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 21504 remote VC label : 21504 local AC OAM State : up local PSN State : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote statuscode : 0x0 BFD for PW : available BFD sessionIndex : 256 BFD state : up manual fault : not set active state : active forwarding entry : exist link state : up local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 Local VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Remote VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy name : -- traffic behavior name : -- PW template name : 1to2 primary or secondary : primary VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x1002004 create time : 0 days, 1 hours, 17 minutes, 55 seconds up time : 0 days, 1 hours, 16 minutes, 47 seconds last change time : 0 days, 1 hours, 16 minutes, 47 seconds VC last up time : 2008-07-24 12:31:31 VC total up time: 0 days, 2 hours, 12 minutes, 51 seconds CKey : 16 NKey : 15 *client interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 is up session state : up AC status : up VC state : up VC ID : 200 VC type : Ethernet destination : 5.5.5.5 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 21505 remote VC label : 21504 local AC OAM state : up local PSN state : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote statuscode : 0x0 BFD for PW : available BFD sessionIndex : 257 BFD state : up manual fault : not set active state : inactive forwarding entry : existent link state : up local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 Local VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Remote VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy name : -- traffic behavior name : -- PW template name : 1to3 primary or secondary : secondary VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x1002006 create time : 0 days, 1 hours, 17 minutes, 42 seconds up time : 0 days, 1 hours, 15 minutes, 55 seconds last change time : 0 days, 1 hours, 15 minutes, 55 seconds VC last up time : 2008-07-24 12:31:31 VC total up time: 0 days, 2 hours, 12 minutes, 51 seconds CKey : 17 NKey : 18 reroute policy : delay 30 s, resume 10 s reason of last reroute : -- time of last reroute : -- days, -- hours, -- minutes, -- seconds delay timer ID : -- residual time :-- resume timer ID : -- residual time :--
Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/1 of PE1 to simulate a fault on the primary PW. Then, CE1 cannot use the primary address to ping CE2's 10.1.1.2. After the secondary PW takes over services, CE1 can use the secondary IP address to successfully ping CE2's 10.1.1.2.
<CE1> ping 10.1.1.2 PING 10.1.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Request time out Request time out Request time out Request time out Request time out --- 10.1.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 0 packet(s) received 100.00% packet loss <CE1> ping 10.1.2.2 PING 10.1.2.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=140 ms Reply from 10.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=160 ms Reply from 10.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=160 ms Reply from 10.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=160 ms Reply from 10.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=160 ms --- 10.1.2.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 140/156/160 ms# Run the display mpls l2vc interface command on each PE. The VC state field of the primary PW is down and the BFD for PW field is unavailable. The VC state field of the secondary PW is up, the BFD for PW field is available, and the BFD state field is up.
<PE1> display mpls l2vc interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 *client interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 is up session state : down AC status : up VC state : down VC ID : 100 VC type : PPP destination : 4.4.4.4 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 21504 remote VC label : 0 local AC OAM State : up local PSN State : up local forwarding state : not forwarding local status code : 0x0 BFD for PW : unavailable manual fault : not set active state : inactive forwarding entry : not exist link state : down local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 Local VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Remote VCCV : none local control word : enable remote control word : none tunnel policy name : -- traffic behavior name : -- PW template name : 1to2 primary or secondary : primary VC tunnel/token info : 0 tunnels/tokens create time : 0 days, 0 hours, 30 minutes, 58 seconds up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 0 minutes, 0 seconds last change time : 0 days, 0 hours, 6 minutes, 46 seconds VC last up time : 2008-07-24 12:31:31 VC total up time: 0 days, 2 hours, 12 minutes, 51 seconds CKey : 16 NKey : 15 *client interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 is up session state : up AC status : up VC state : up VC ID : 200 VC type : PPP destination : 5.5.5.5 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 21505 remote VC label : 21504 local AC OAM state : up local PSN state : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote statuscode : 0x0 BFD for PW : available BFD sessionIndex : 257 BFD state : up manual fault : not set active state : active forwarding entry : existent link state : up local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 Local VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd Remote VCCV : cw alert lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy name : -- traffic behavior name : -- PW template name : 1to3 primary or secondary : secondary VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x1002008 create time : 0 days, 0 hours, 30 minutes, 58 seconds up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 25 minutes, 12 seconds last change time : 0 days, 0 hours, 25 minutes, 12 seconds VC last up time : 2008-07-24 12:31:31 VC total up time: 0 days, 2 hours, 12 minutes, 51 seconds CKey : 17 NKey : 18 reroute policy : delay 30 s, resume 10 s reason of last reroute : -- time of last reroute : -- days, -- hours, -- minutes, -- seconds delay timer ID : -- residual time :-- resume timer ID : -- residual time :--
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.252 sub # returnPE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # bfd # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 mpls # mpls l2vpn # pw-template 1to2 peer-address 4.4.4.4 control-word # pw-template 1to3 peer-address 5.5.5.5 control-word # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer 4.4.4.4 remote-ip 4.4.4.4 # mpls ldp remote-peer 5.5.5.5 remote-ip 5.5.5.5 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown mpls l2vc pw-template 1to2 100 mpls l2vc pw-template 1to3 200 secondary # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.3 # bfd 1to2 bind pw interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 discriminator local 12 discriminator remote 21 commit # bfd 1to3 bind pw interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 secondary discriminator local 13 discriminator remote 31 commit # return
P1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return
P2 configuration file
# sysname P2 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.5.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # bfd # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 mpls # mpls l2vpn # pw-template 2to1 peer-address 1.1.1.1 control-word # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer 1.1.1.1 remote-ip 1.1.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown mpls l2vc pw-template 2to1 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.3 # bfd 2to1 bind pw interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 discriminator local 21 discriminator remote 12 commit # return
PE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # bfd # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 mpls # mpls l2vpn # pw-template 3to1 peer-address 1.1.1.1 control-word # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer 1.1.1.1 remote-ip 1.1.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.5.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown mpls l2vc pw-template 3to1 200 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.3 # bfd 3to1 bind pw interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 discriminator local 31 discriminator remote 13 commit # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252 # return