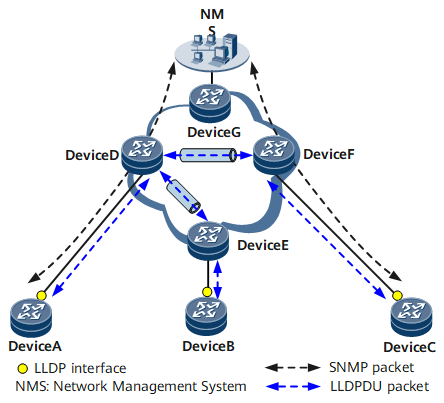
LLDP Applications in Multi-Neighbor Networking
Networking Description
In multi-neighbor networking, each interface is connected to multiple remote neighboring devices. In the multi-neighbor networking shown in Figure 1, the network connected to Device A, Device B, and Device C is unknown. Devices on this unknown network may have LLDP disabled or may not need to be managed by the NMS, but they can still transparently transmit LLDP packets. Interfaces on Device A, Device B, and Device C are connected to multiple remote neighboring devices.
Feature Deployment
After LLDP is configured on Device A, Device B, and Device C, an administrator can use the NMS to obtain Layer 2 configuration information about these devices, collect detailed network topology information, and determine whether a configuration conflict exists. LLDP helps make network communications more secure and stable.