Multicast over P2MP TE Tunnels
Using point-to-multipoint (P2MP) Traffic Engineering (TE) tunnels to carry multicast services on an IP/Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) backbone network provides high TE capabilities and reliability and reduces operational expenditure (OPEX).
Background
- IP multicast technology: It can be deployed on point-to-point (P2P) networks to run multicast services, reducing network upgrade and maintenance costs. Similar to IP unicast, IP multicast does not support QoS or traffic planning and has low reliability. Multicast applications place high demands on real-time transmission and reliability, and IP multicast technology cannot meet these requirements.
- Establishing a dedicated multicast network: A dedicated multicast network is usually constructed over Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH). SONET/SDH has high reliability and provides a high transmission rate. However, such a network is expensive to construct, incurs significant OPEX, and must be maintained separately.
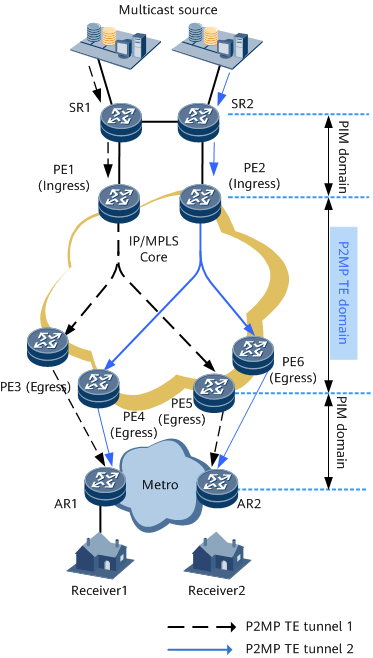
Multicast over P2MP TE tunnels can meet the carriers' requirements by establishing tree tunnels to transmit multicast data. It has the advantages of high IP multicast packet transmission efficiency and assured MPLS TE end-to-end (E2E) QoS.
Benefits
Improves network bandwidth utilization.
Provides sufficient bandwidth for multicast services.
Simplifies network deployment because multicast protocols, such as PIM, do not need to be deployed on core devices on the backbone network.
Related Concepts
P2MP TE data forwarding is similar to IP multicast data forwarding. A branch node copies MPLS packets, performs label operations, and sends only one packet copy over every sub-LSP. This process increases network bandwidth resource utilization.
For details on P2MP TE concepts, see Related Concepts in the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series Feature Description - MPLS.
Technologies Used by Multicast over P2MP TE Tunnels
Ingresses
The P2MP tunnel interfaces of the ingresses (PE1 and PE2) direct multicast data to a P2MP TE tunnel.
Egresses
The egresses (PE3, PE4, PE5, and PE6) must be configured to ignore the unicast reverse path forwarding (URPF) check. Whether to configure multicast source proxy on the egresses is based on the location of the rendezvous point (RP).
Ignoring the URPF check
The egresses must be configured to ignore the URPF check during multicast traffic forwarding.
Multicast source proxy
In a multicast over P2MP TE scenario where PIM-SM is used, if an RP is deployed at the egress side, the multicast source cannot send a Register message to the RP because it cannot find an available route to the RP. In this case, multicast source proxy can be used to enable the egress to register multicast source information with the RP.
If a multicast data packet for a group in the any-source multicast (ASM) address range is directed to an egress which is not directly connected to the multicast source and does not function as the RP to which the group corresponds, the multicast data packet stops being forwarded. As a result, downstream hosts cannot receive these multicast data packets. Multicast source proxy can be used to address this problem. Multicast source proxy enables the egress to send a Register message to the RP in a PIM domain, such as AR1 or AR2.