MSTP Fast Convergence
Ordinary P/A
The ordinary P/A mechanism supported by MSTP is implemented in the same manner as that supported by Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). For details about the P/A mechanism supported by RSTP, see RSTP Implementation.
Enhanced P/A
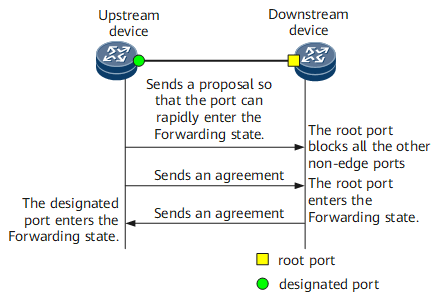
As shown in Figure 1, in MSTP, the P/A mechanism works as follows:
The upstream device sends a proposal to the downstream device, indicating that the port connecting to the downstream device wants to enter the Forwarding state as soon as possible. After receiving this Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU), the downstream device sets its port connecting to the upstream device to the root port, and blocks all non-edge ports.
The upstream device continues to send an agreement. After receiving this BPDU, the root port enters the Forwarding state.
The downstream device replies with an agreement. After receiving this BPDU, the upstream device sets its port connecting to the downstream device to the designated port, and the port enters the Forwarding state.
By default, Huawei devices use the enhanced P/A mechanism. If a Huawei device needs to communicate with a non-Huawei device that uses the ordinary P/A mechanism, run the stp no-agreement-check command to configure the Huawei device to use the ordinary P/A mechanism. In this manner, these two devices can communicate with each other.