VPLS MAC Ping Test
Overview
A VPLS MAC ping test is used to detect whether a specified destination MAC address exists and whether the path across the VPLS network to the specified destination MAC address is reachable. At present, only the peer bridge MAC address can be pinged.
Test Process
On the network shown in Figure 1, the general VPLS MAC ping test process is as follows:
The VPLS MAC ping test instance on the local PE constructs an MPLS Echo Request packet and adds network address 127.0.0.0/8 to the IP header as the destination IP address. Then, the test instance searches the MAC address table on the local PE for a MAC forwarding entry corresponding to the destination MAC address. If a MAC forwarding entry learned from the PW side is found, the test instance sends the MPLS Echo Request packet to the corresponding PW. Otherwise, the test instance broadcasts the MPLS Echo Request packet to all PWs in the specified VSI. The VSI and destination MAC address must be specified before a VPLS MAC ping test instance is run. The destination MAC address can be either the remote PE's bridge MAC address or the CE's MAC address.
The remote PE listens to port 3503 for the MPLS Echo Request packet and returns an MPLS Echo Reply packet as the response.
If the destination MAC address is a CE's MAC address, the MPLS Echo Request packet will not be forwarded to the CE. Instead, the destination MAC address will be checked on the PE to which the CE connects. If the destination MAC address can be found in the PE's MAC address table, the VPLS MAC ping test is regarded as successful; otherwise, the test is regarded as unsuccessful.
The local PE can then calculate the communication time between itself and the remote PE by subtracting the time at which the local PE sends the MPLS Echo Request packet from the time at which the local PE receives the MPLS Echo Reply packet. The communication time clearly reflects VPLS network performance.
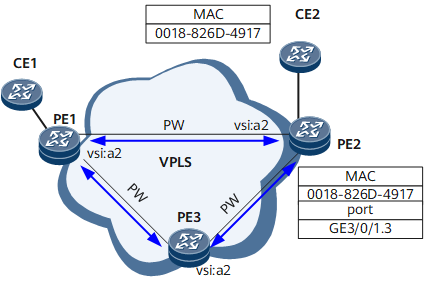
On the network shown in Figure 1, if PE1 initiates the VPLS MAC ping test, the test process is as follows (assume that in the VPLS MAC ping test instance, the specified VSI is a2 and the specified destination MAC address is 00e0-fc12-3456, CE2's MAC address):
The VPLS MAC ping test instance constructs an MPLS Echo Request packet and searches PE1's MAC address table for a MAC forwarding entry. After failing to find a matching MAC forwarding entry, the test instance broadcasts the MPLS Echo Request packet to all PWs in the specified VSI.
Upon receipt of the MPLS Echo Request packet, PE3 compares the destination MAC address of the packet with its bridge MAC address. After finding that the two MAC addresses are different, PE3 searches its MAC address table for a MAC forwarding entry corresponding to the destination MAC address. After failing to find a matching MAC forwarding entry, PE3 stops forwarding the MPLS Echo Request packet according to the split horizon principle.
Upon receipt of the MPLS Echo Request packet, PE2 also compares the destination MAC address of the packet with its bridge MAC address. After finding that the two MAC addresses are different, PE2 searches its MAC address table for a MAC forwarding entry corresponding to the destination MAC address. After successfully finding a matching MAC forwarding entry, PE2 returns an MPLS Echo Reply packet.
Usage Scenario
VPLS MAC ping tests can be used in both conventional VPLS and HVPLS scenarios.
Benefits
When a link fault occurs, you can perform a VPLS MAC ping test to detect VPLS network connectivity.