VPLS Multi-homing
Background
To deliver high-reliability services over a VPLS network, carriers usually dual-home a CE to two PEs through redundant links. While providing link-level protection, the dual-homing mechanism also brings in the risk of routing loops. Currently, E-Trunk multi-homing or STP over VPLS is used to prevent routing loops. However, E-Trunk multi-homing is not widely supported by non-Huawei devices, and STP over VPLS introduces high routing costs during real-time loop detection. VPLS multi-homing adjusts link priorities to prevent routing loops. It ensures that one access link of a multi-homed CE is in the active state and the other access links are in the blocked state.
Related Concepts
VPLS multi-homing uses BGP to transmit multi-homing site information. It enhances standard BGP VPLS and improves reliability and applies to scenarios where a CE is multi-homed to PEs.
Concept |
Description |
|---|---|
MH-ID |
A multi-homing ID that uniquely identifies a multi-homing site |
Optimal site |
Preferred multi-homing site used for PW establishment |
Implementation
In VPLS multi-homing implementation, after a multi-homing site is configured on a PE accessed by a multi-homed CE, the PE advertises a BGP Update message carrying its multi-homing site information (including the MH-ID) to the other PEs in the VPLS domain. Upon receipt of the BGP Update message, PEs with the same MH-ID as that carried in the BGP Update message start an election process to determine which PE is the preferred one. After the preferred PE is elected, the access links between the multi-homed CE and the non-preferred PEs are blocked to prevent routing loops.
- AC status (ACS): For PEs with the same MH-ID, the ACS value may be either of the following:
- 1: The AC between a multi-homed CE and a PE is Down.
- 0: The AC between a multi-homed CE and a PE is Up.
The link whose ACS is 0 has a higher priority than the link whose ACS is 1.
- Preference (PREF): A larger PREF value indicates a higher link priority. The value must be configured.
- PE's router ID (PE-ID): If no BGP router ID is configured, the system router ID is used by default. If a BGP router ID is configured, it is used as the PE-ID.
A lower PE-ID indicates a higher link priority.
If a link between a multi-homed CE and a PE fails, the PE advertises a BGP Update message that carries ACS, PREF, and PE-ID information to the other PEs in the VPLS domain. Then, PEs with the same MH-ID as that carried in the BGP Update message start an election process to select a preferred link.
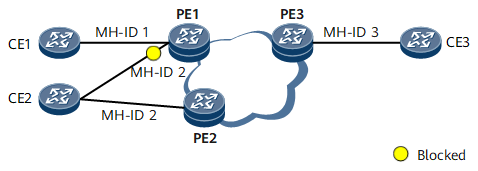
- Blocks the AC interface to prevent routing loops. After PE1 receives a BGP Update message from PE2, PE1 finds PE2's multi-homing site with the same MH-ID (2) as a multi-homing site on itself. Therefore, PE1 compares the ACS, PREF, and PE-ID values of the two sites. Because PE1's MH-ID 2 has a lower priority than PE2's MH-ID 2, PE1 blocks the AC interface of MH-ID 2. After PE2 receives a BGP Update message from PE1, PE2 also finds PE1's multi-homing site with MH-ID 2 and compares the ACS, PREF, and PE-ID values of the two sites. Because PE1's MH-ID 2 has a lower priority than PE2's MH-ID 2, PE2 does not take any action.
- PE1 selects MH-ID 1 as the optimal site, PE2 MH-ID 2, and PE3 MH-ID 3.
- Establishes PWs between the optimal sites.