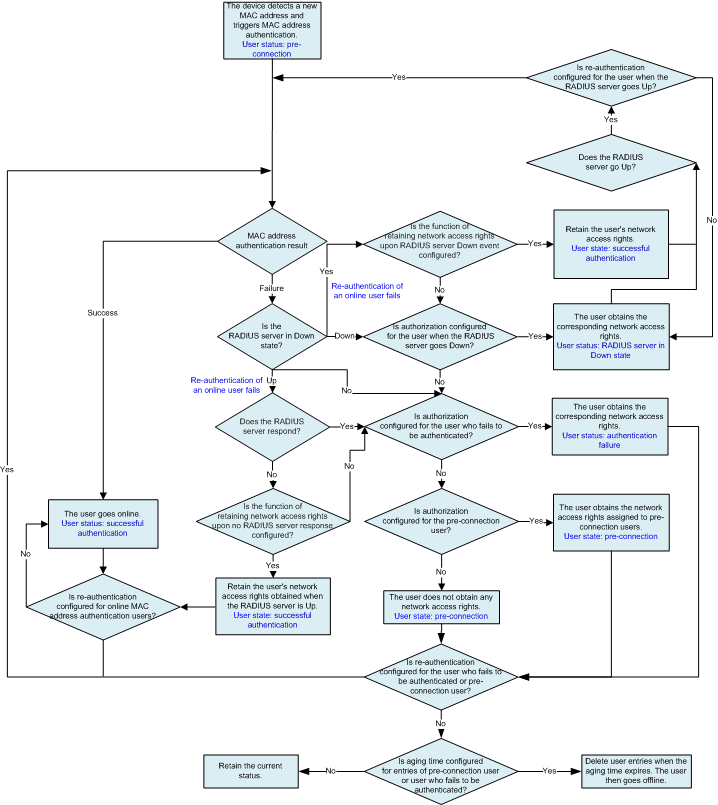
Logical Process of MAC Address Authentication
Figure 1 shows the processing logic of the access device during MAC address authentication. RADIUS authentication is used as an example.
- After detecting a new MAC address, the access device triggers MAC address authentication for the user.
- The access device sends a RADIUS Access-Request packet to the RADIUS server, requesting the RADIUS server to perform MAC address authentication for the user (for details, see RADIUS Server Selection Mechanism and MAC Address Authentication Process).
- If the MAC address authentication succeeds, the user goes online.
- If the MAC address authentication fails and the RADIUS server is in Down state (for details, see RADIUS Server Status Detection), the access device checks whether it is configured to authorize users when the RADIUS server is in Down state, to authorize users who fail to be authenticated, and to authorize pre-connection users (for details, see NAC Escape Mechanism). If so, the user obtains the corresponding network access rights; if not, the user does not have any network access rights.
- If the MAC address authentication fails and the RADIUS server is in Up state, the access device checks whether it is configured to authorize users who fail to be authenticated and to authorize pre-connection users. If yes, the user obtains the corresponding network access rights; if not, the user does not have any network access rights.
- For users in abnormal authentication state, the access device can be configured to re-authenticate the users so that they can obtain network access rights as soon as possible. For users who have passed MAC address authentication, re-authentication can ensure the validity of user identities (for details, see MAC Address Re-authentication).
- If re-authentication after a successful authentication fails and the authentication server is in Down state, the access device checks the configuration of retaining the user's network access rights upon the authentication server Down event, the authorization configuration upon the authentication server Down event, the authorization configuration upon authentication failures, and the authorization configuration for pre-connection users in sequence, and authorizes the user accordingly. If the RADIUS server is in Up state but does not respond, the access device checks the configuration of retaining the user's network access rights upon no server response, the authorization configuration upon authentication failures, and the authorization configuration for pre-connection users in sequence, and authorizes the user accordingly.