This section describes how to configure EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE.
Usage Scenario
EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE uses public SRv6 BE to carry EVPN L3VPN services. The implementation of EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE involves deploying SRv6 BE, implementing EVPN route interworking, and forwarding data.
As shown in Figure 1, PE1 and PE2 communicate through an IPv6 public network. SRv6 BE is deployed on the public IPv6 network to carry EVPN L3VPN services.
Figure 1 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE networking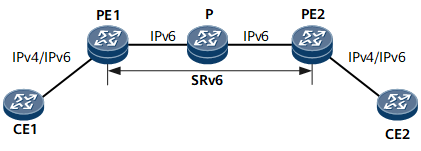
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE, complete the following tasks:
Procedure
- Configure IPv6 IS-IS on each PE and P. For configuration details, see Configuring Basic IPv6 IS-IS Functions.
- Configure an L3VPN instance.
For IPv4 services, configure an IPv4 L3VPN instance.
Run ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
A VPN instance is created, and the VPN instance view is displayed.
Run ipv4-family
The VPN instance IPv4 address family is enabled, and the view of this address family is displayed.
Run route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
An RD is configured for the VPN instance IPv4 address family.
Run vpn-target vpn-target &<1-8> [ both | export-extcommunity | import-extcommunity ] evpn
VPN targets are added to the VPN target list of the VPN instance IPv4 address family, so that routes of the VPN instance can be added to the routing table of the EVPN instance configured with a matching VPN target.
(Optional) Run tnl-policy policy-name evpn
The EVPN routes imported to the VPN instance IPv4 address family are enabled to be associated with a tunnel policy.
(Optional) Run import route-policy policy-name evpn
The VPN instance IPv4 address family is associated with an import route-policy that is used to filter routes imported from the EVPN instance to the VPN instance IPv4 address family. To control route import more precisely, specify an import route-policy to filter routes and set route attributes for routes that meet the filter criteria.
(Optional) Run export route-policy policy-name evpn
The VPN instance IPv4 address family is associated with an export route-policy that is used to filter routes advertised from the VPN instance IPv4 address family to the EVPN instance. To control route advertisement more precisely, specify an export route-policy to filter routes and set route attributes for routes that meet the filter criteria.
Run quit
Exit the VPN instance IPv4 address family view.
Run quit
Exit the VPN instance view.
For IPv6 services, configure an IPv6 L3VPN instance.
Run ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
A VPN instance is created, and the VPN instance view is displayed.
Run ipv6-family
The VPN instance IPv6 address family is enabled, and the view of this address family is displayed.
Run route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
An RD is configured for the VPN instance IPv6 address family.
Run vpn-target vpn-target &<1-8> [ both | export-extcommunity | import-extcommunity ] evpn
VPN targets are added to the VPN target list of the VPN instance IPv6 address family, so that routes of the VPN instance can be added to the routing table of the EVPN instance configured with a matching VPN target.
(Optional) Run tnl-policy policy-name evpn
The EVPN routes imported to the VPN instance IPv6 address family are enabled to be associated with a tunnel policy.
(Optional) Run import route-policy policy-name evpn
The VPN instance IPv6 address family is associated with an import route-policy that is used to filter routes imported from the EVPN instance to the VPN instance IPv6 address family. To control route import more precisely, specify an import route-policy to filter routes and set route attributes for routes that meet the filter criteria.
(Optional) Run export route-policy policy-name evpn
The VPN instance IPv6 address family is associated with an export route-policy that is used to filter routes advertised from the VPN instance IPv6 address family to the EVPN instance. To control route advertisement more precisely, specify an export route-policy to filter routes and set route attributes for routes that meet the filter criteria.
Run quit
Exit the VPN instance IPv6 address family view.
Run quit
Exit the VPN instance view.
- Bind the L3VPN instance to an access-side interface.
- Run interface interface-type interface-number
The interface view is displayed.
- Run ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
The L3VPN instance is bound to the interface.
- (Optional) Run ipv6 enable
IPv6 is enabled on the interface.
- Run ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } or ipv6 address { ipv6-address prefix-length | ipv6-address/prefix-length }
An IPv4/IPv6 address is configured for the interface.
- Run quit
Exit the interface view.
- Configure BGP EVPN peer relationships.

If a BGP RR needs to be configured on the network, establish BGP EVPN peer relationships between all the PEs and the RR.
- Run bgp { as-number-plain | as-number-dot }
BGP is enabled, and the BGP view is displayed.
- Run peer { ipv6-address | group-name } as-number { as-number-plain | as-number-dot }
The remote PE is configured as a peer.
- (Optional) Run peer { ipv6-address | group-name } connect-interface interface-type interface-number
A source interface and a source address are specified to set up a TCP connection with the BGP peer.

If loopback interfaces are used to establish a BGP connection, you are advised to run the peer connect-interface command on both ends to ensure the connectivity. If this command is run on one end only, the BGP connection may fail to be established.
- Run ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn-instance-name or ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
The BGP-VPN instance IPv4/IPv6 address family view is displayed.
- Run import-route { direct | isis process-id | ospf process-id | rip process-id | static | ospfv3 process-id | ripng process-id } [ med med | route-policy route-policy-name ] *
Other protocol routes are imported to the BGP-VPN instance IPv4/IPv6 address family. To advertise host IP routes, configure import of direct routes. To advertise routes on the network segment where the host resides, use a dynamic routing protocol (such as OSPF) to advertise routes on the network segment and configure the dynamic routing protocol to import routes.
- Run advertise l2vpn evpn [ import-route-multipath ]
The device is enabled to advertise IP prefix routes. IP prefix routes are used to advertise host IP routes as well as routes on the network segment where the host resides.
To implement SID-based load balancing, specify the import-route-multipath parameter for the device to advertise all IP prefix routes with the same destination address.
- Run quit
Exit the BGP-VPN instance IPv4/IPv6 address family view.
- Run l2vpn-family evpn
The BGP EVPN address family view is displayed.
- Run peer { ipv6-address | group-name } enable
The device is enabled to exchange EVPN routes with the specified peer or peer group.
- (Optional) Run nexthop recursive-lookup default-route The device is enabled to send packets over a default route when the recursive next-hop address is unavailable.
In an EVPN over SRv6 BE scenario, problems such as configuration errors or faults may cause the PE at one end to fail to recurse services to SRv6 BE due to route unreachability, resulting in a service forwarding failure. To prevent this, run the nexthop recursive-lookup default-route command on the local PE and configure the remote PE to send a default route to the local PE. In this way, if the next hop of a specific route on the local PE is unreachable, services can be steered to an SRv6 BE path through recursion to the default route, ensuring service continuity.
- Run quit
Exit the BGP EVPN address family view.
- Run quit
Exit the BGP view.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Configure basic SRv6 functions.
- (Optional) Run evpn srv6 next-header-field { 59 | 143 }
A value is set for the Next Header field in an SRv6 extension header.
- Run segment-routing ipv6
SRv6 is enabled, and the SRv6 view is displayed.
- Run encapsulation source-address ipv6-address [ ip-ttl ttl-value ]
A source address is specified for SRv6 EVPN encapsulation.
- Run locator locator-name [ ipv6-prefix ipv6-address prefix-length [ static static-length | args args-length ] * ]
An SRv6 locator is configured.
- (Optional) Run opcode func-opcode { end-dt4 | end-dt6 } vpn-instance vpn-instance-name evpn
A static SID operation code (opcode) is configured. The end-dt4 parameter is used for IPv4 services, and the end-dt6 parameter is used for IPv6 services.
Alternatively, run the opcode func-opcode { end-dx4 | end-dx6 } vpn-instance vpn-instance-name evpn interface interface-type interface-number nexthop nexthop-address command to configure a static SID opcode. The end-dx4 parameter is used for IPv4 services, and the end-dx6 parameter is used for IPv6 services.
In EVPN scenarios, end-dx4 and end-dx6 are used to allocate SIDs based on interfaces to which VPN instances are bound, and end-dt4 and end-dt6 are used to allocate SIDs based on VPN instances.
The preceding SIDs can be either dynamically allocated by BGP or manually configured. If you want to enable dynamic SID allocation using the segment-routing ipv6 locator locator-name command, skip this step.
- Run quit
Exit the SRv6 locator view.
- Run quit
Exit the SRv6 view.
- Enable IS-IS SRv6 on PEs.
- Run isis [ process-id ]
The IS-IS view is displayed.
- Run ipv6 enable topology ipv6
The IPv6 capability is enabled for the IS-IS process in the IPv6 topology.
- Run segment-routing ipv6 locator locator-name [ auto-sid-disable ]
IS-IS SRv6 is enabled.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Run quit
Exit the IS-IS view.
- Configure EVPN routes on PEs to carry SIDs and recurse to SRv6 BE paths based on the SIDs.
- Run bgp { as-number-plain | as-number-dot }
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run l2vpn-family evpn
The BGP EVPN address family view is displayed.
- Run peer { ipv6-address | group-name } advertise encap-type srv6 [ advertise-srv6-locator ]
The device is enabled to send EVPN routes carrying SRv6-encapsulated attributes to the specified peer or peer group.
In a scenario where BFD is used to check locator reachability, after locator routes are summarized by a P device between local and remote PEs, the remote PE can learn only the summary locator route, not the locator on the local PE. This leads to a BFD failure. To address this issue, configure the advertise-srv6-locator parameter in the command to allow the local PE to carry locator length information in the EVPN route advertised to the remote PE. In this way, after receiving the EVPN route, the remote PE can calculate the locator on the local PE, enabling BFD to take effect.
- Run quit
Exit the BGP EVPN address family view.
- Run ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn-instance-name or ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
The BGP-VPN instance IPv4/IPv6 address family view is displayed.
- Run segment-routing ipv6 locator locator-name evpn
The device is enabled to add SIDs to VPN routes before sending the routes to EVPN.
- Run segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
The device is enabled to perform route recursion based on the SIDs carried by EVPN routes.
- (Optional) Configure the device to allocate SIDs to BGP VPN routes based on next hops, thereby implementing SID-based load balancing.
To configure the device to allocate SIDs to BGP VPN routes based on all next hops:
To configure the device to allocate a SID to a BGP VPN route with a specified next hop:
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Verifying the Configuration
After configuring EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE, verify the configuration.
Run the display bgp vpnv4 { all | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name } routing-table [ network [ prefix-length ] ] command to check BGP VPNv4 route information.
Run the display bgp vpnv6 { all | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name } routing-table [ network [ prefix-length ] ] command to check BGP VPNv6 route information.
- Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table prefix-route prefix command to check EVPN IP prefix route information.
Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn-instance-name or display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn-instance-name command to check information about the VPN routes received from the remote device.

