Configuring L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE
This section describes how to configure L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE.
Context
L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE allows SRv6 BE paths on a public network to carry L3VPNv6 data. The key implementation of L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE involves establishing SRv6 BE paths, advertising VPN routes, and forwarding data.
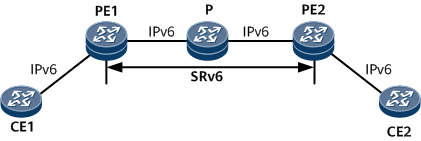
Figure 1 shows an example where an IPv6 public network is established between PE1 and PE2 and the involved VPNs are also IPv6 networks. SRv6 BE paths can be deployed on the IPv6 public network to carry L3VPNv6 services.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE, complete the following tasks:
Configure a link-layer protocol.
Configure network-layer addresses for interfaces to ensure that neighboring devices are reachable at the network layer.
Procedure
- Configure IPv6 IS-IS on the PEs and P. For configuration details, see Configuring Basic IPv6 IS-IS Functions.
- Configure a VPN instance on each PE and enable the IPv6 address family.
- Configure PE-CE IPv6 route exchange. For configuration details, see Configuring Route Exchange Between PEs and CEs.
- Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
- Configure basic SRv6 functions.
- Enable IS-IS SRv6 on each PE.
- Configure each PE to carry SIDs in VPN routes and recurse the routes to SRv6 BE paths based on the SIDs.
Verifying the Configuration
After configuring L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE, verify the configuration.
Run the display segment-routing ipv6 locator [ locator-name ] verbose command to check SRv6 locator information.
Run the display segment-routing ipv6 local-sid { end | end-x | end-dt6 } [ sid ] forwarding command to check information about the SRv6 local SID table.
Run the display bgp vpnv6 { all | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name } routing-table ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] command to check BGP VPNv6 routing information.
Run the ping ipv6 command to check the connectivity between CEs.