Example for Configuring IS-IS to Interact with BGP
This section describes how to configure IS-IS to interact with BGP, including configuring BGP and IS-IS to import routes from each other.
Networking Requirements
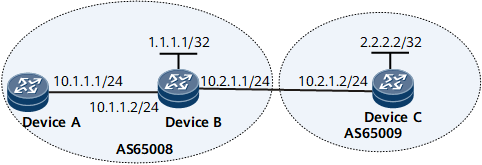
In Figure 1:
Device A and Device B belong to the same AS, and the IS-IS neighbor relationship is established between the two devices. BGP is not enabled on Device A.
An EBGP connection is established between Device B and Device C. When IS-IS imports BGP routes, a routing policy is required to change the route cost.
Device Name |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
Device B |
Loopback0 |
192.168.0.1/32 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/1/8 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
Device C |
Loopback0 |
192.168.0.2/32 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable IS-IS and specify NETs on device A and device B.
Configure an EBGP connection on device B and device C.
Configure IS-IS and BGP to import routes from each other on Device B, and then check the routes.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Area addresses of Device A and Device B
Router ID and AS number of Device B
Router ID and AS number of Device C
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic IS-IS functions.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] isis 1 [*DeviceA-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*DeviceA-isis-1] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] isis 1 [*DeviceB-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*DeviceB-isis-1] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure an EBGP connection.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65008 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] network 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 65009 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceC-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] network 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv4] commit
- Configure IS-IS to import BGP routes.
# Configure a static route on Device C.
[~DeviceC] ip route-static 172.16.1.1 32 NULL 0 [*DeviceC] commit
# On Device C, configure BGP to import the static route.
[~DeviceC] bgp 65009 [~DeviceC-bgp] import-route static [*DeviceC-bgp] commit
# On Device B, configure IS-IS to import the BGP route.
[~DeviceB] isis 1 [~DeviceB-isis-1] import-route bgp [*DeviceB-isis-1] commit [~DeviceB-isis-1] quit
# Display the routing table of Device A. The command shows that IS-IS successfully imports the BGP route 172.16.1.1/32.
[~DeviceA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: _public_ Destinations : 11 Routes : 11 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 172.16.1.1/32 ISIS-L2 15 74 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
# On Device B, configure the AS_Path filter, and apply the filter in the routing policy named RTC.
[~DeviceB] ip as-path-filter 1 permit 65009 [*DeviceB] route-policy RTC permit node 0 [*DeviceB-route-policy] if-match as-path-filter 1 [*DeviceB-route-policy] apply cost 20 [*DeviceB-route-policy] commit [~DeviceB-route-policy] quit
# On Device B, configure IS-IS to import the BGP route.
[~DeviceB] isis 1 [~DeviceB-isis-1] import-route bgp route-policy RTC [*DeviceB-isis-1] commit [~DeviceB-isis-1] quit
# Display the routing table of device A. The command shows that the AS_Path filter has been applied and that the cost of the imported route 172.16.1.1/32 changes from 74 to 94.
[~DeviceA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: _public_ Destinations : 11 Routes : 11 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 172.16.1.1/32 ISIS-L2 15 94 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
- Configure BGP to import IS-IS routes.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65008 [~DeviceB-bgp] import-route isis 1 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Display the routing table of Device C. The command shows that BGP has imported the IS-IS route 10.1.1.0/24.
[~DeviceC] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: _public_ Destinations : 7 Routes : 7 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 192.168.0.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0 10.1.1.0/24 EBGP 255 0 D 10.2.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.2.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 172.16.1.1/32 Static 60 0 DB 0.0.0.0 NULL0 192.168.0.1/32 EBGP 255 0 RD 10.2.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # isis 1 import-route bgp route-policy RTC network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65008 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 65009 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 import-route static import-route isis 1 peer 10.2.1.2 enable # route-policy RTC permit node 0 if-match as-path-filter 1 apply cost 20 # ip as-path-filter 1 permit 65009 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65009 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 import-route static peer 10.2.1.1 enable # ip route-static 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.255 NULL0 # return