Example for Configuring Static BFD for IS-IS
This section describes how to configure static BFD for IS-IS, including configuring BFD parameters and enabling static BFD.
Networking Requirements
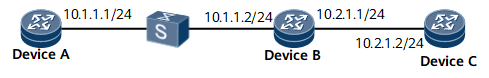
In Figure 1:
Device A and Device B are connected through a Layer 2 switch.
IS-IS runs on Device A, Device B, and Device C.
BFD is configured to detect the IS-IS neighbor relationship between Device A and Device B. If the link between Device A and Device B fails, BFD can fast detect the fault and notify it to IS-IS.
Device Name |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
Device B |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
GE0/1/8 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
Device C |
GE0/1/0 |
10.2.1.2/24 |

BFD for IS-IS cannot be used to detect the multi-hop link between Device A and Device C because the IS-IS neighbor relationship is not established between Device A and Device C.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic IS-IS functions on each router.
Enable BFD on Device A and Device B.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IS-IS process ID
Area addresses of Device A, Device B, and Device C
Levels of Device A, Device B, and Device C
Name of the BFD session established between Device A and Device B and peer IP address to be detected by BFD
Local and remote discriminators of the BFD session established between Device A and Device B
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for the interface on each router. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic IS-IS functions.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] isis 1 [*DeviceA-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*DeviceA-isis-1] network-entity aa.1111.1111.1111.00 [*DeviceA-isis-1] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] isis 1 [*DeviceB-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*DeviceB-isis-1] network-entity aa.2222.2222.2222.00 [*DeviceB-isis-1] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] isis 1 [*DeviceC-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*DeviceC-isis-1] network-entity aa.3333.3333.3333.00 [*DeviceC-isis-1] quit [*DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# After the preceding configurations. The command shows that the neighbor relationship has been established between Device A and Device B.
[~DeviceA] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2222.2222.2222 GE0/1/0 2222.2222.2222.00 Up 23s L2 64 Total Peer(s): 1
The IS-IS routing table of Device A has the routes to Device B and Device C.
[~DeviceA] display isis route Route information for ISIS(1) ----------------------------- ISIS(1) Level-2 Forwarding Table -------------------------------- IPV4 Destination IntCost ExtCost ExitInterface NextHop Flags ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10.1.1.0/24 10 NULL GE0/1/0 Direct D/-/L/- 10.2.1.0/24 20 NULL GE0/1/0 10.1.1.2 A/-/-/- Flags: D-Direct, A-Added to URT, L-Advertised in LSPs, S-IGP Shortcut, U-Up/Down Bit Set Protect Type: L-Link Protect, N-Node Protect
- Configure BFD.
# Enable BFD and configure a BFD session on Device A.
[~DeviceA] bfd [*DeviceA-bfd] quit [*DeviceA] bfd atob bind peer-ip 10.1.1.2 interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*DeviceA-bfd-session-atob] discriminator local 1 [*DeviceA-bfd-session-atob] discriminator remote 2 [*DeviceA-bfd-session-atob] commit [~DeviceA-bfd-session-atob] quit
# Enable BFD and configure a BFD session on Device B.
[~DeviceB] bfd [*DeviceB-bfd] quit [*DeviceB] bfd btoa bind peer-ip 10.1.1.1 interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*DeviceB-bfd-session-btoa] discriminator local 2 [*DeviceB-bfd-session-btoa] discriminator remote 1 [*DeviceB-bfd-session-btoa] commit [~DeviceB-bfd-session-btoa] quit
# After the preceding configurations, run the display bfd session command on Device A or Device B. The command shows that the BFD session has been Up.
Use the command output on Device A as an example.
[~DeviceA] display bfd session all (w): State in WTR (*): State is invalid ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Local Remote PeerIpAddr State Type Interface Name ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1 2 10.1.1.2 Up S_IP_IF GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Total UP/DOWN Session Number : 1/0
- Enable static BFD on the IS-IS interface.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis bfd static [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~DeviceA] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis bfd static [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Enable debugging on Device A.
<DeviceA> debugging isis adjacency <DeviceA> debugging isis circuit-information <DeviceA> terminal debugging
# Run the shutdown command on Gigabit Ethernet 0/1/0 of Device B to simulate a link fault.
[~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] shutdown [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit
# Display the logs on Device A. The command output shows that IS-IS has deleted the neighbor relationship between Device A and Device B after BFD notifies the fault.
#80/active/IsisAdjacencyChange/Major/occurredTime:2011-03-09 04:17:07/-/-/alarmI D:0x08960007/VS=0:ISIS adjacency state change. (SysInstance=1, SysLevel=1, CircI ndex=2, CircIfIndex=20, LspId=2222.2222.2222.00.00, AdjState=1, IfIndex=20, IfNa me=GE0/1/0, Reason=BFD detected that the neighbor went Down, SubReason=14)
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # bfd # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity aa.1111.1111.1111.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 isis bfd static # bfd atob bind peer-ip 10.1.1.2 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 discriminator local 1 discriminator remote 2 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # bfd # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity aa.2222.2222.2222.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 isis bfd static # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # bfd btoa bind peer-ip 10.1.1.1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 discriminator local 2 discriminator remote 1 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # isis 1 is-level level-2 network-entity aa.3333.3333.3333.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # return