Associating the VPWS PW Status with the VPNv6 Route Status
Associating the VPWS PW status with the VPNv6 route status prevents traffic loss caused by a failure to detect link failures.
Context
Usage Scenario
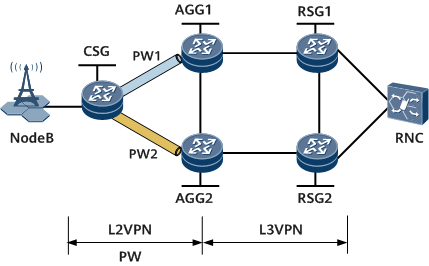
On the network shown in Figure 1, a PW is established between the CSG and each AGG. PW1 is the primary PW, and PW2 is the secondary PW. A BGP VPNv6 peer relationship is established between AGG1 and RSG1, between AGG2 and RSG2, and between AGG1 and AGG2. A VE-Group consisting of one L2VE interface and one L3VE interface is configured on each AGG. The L3VE interface on an AGG is bound to the VPN instance on that AGG.
When no fault occurs, the CSG sends traffic to RSG1 through AGG1 along PW1. If both links between AGG1 and RSG1 and between AGG1 and AGG2 fail and the CSG cannot detect the link failures, the CSG still sends traffic to AGG1, and as a result, traffic loss occurs.
To resolve this problem, configure AGG1 to associate the PW status with the VPNv6 route status. If the link between AGG1 and RSG1 and the link between AGG1 and AGG2 fail, the VPNv6 route status becomes down. AGG1 sets the corresponding VPWS PW status to down and instructs the CSG to perform a primary/secondary PW switchover. Then, the CSG switches upstream traffic to the path CSG -> AGG2 -> RSG2 -> RSG1, preventing traffic loss caused by the link failures.
Pre-configuration Tasks
- Configure data link layer protocol parameters and IP addresses for interfaces to ensure that the link layer protocol of each interface is up.
- Configure basic MPLS functions and public network tunnels.
- Configure PWE3. For configuration details, see Configuring LDP VPWS.
- Configure an L2VPN to access an L3VPN. For configuration details, see VPWS Accessing a Public Network or L3VPN.
- Configure BFD to detect public network link faults. For configuration details, see Configuring BFD to Detect Public Network Link Faults.
Procedure
- Configure each RSG to advertise VPNv6 routes to its BGP VPNv6 peer.
- Configure AGG1 to associate the PW status with the VPNv6 route status.
Verifying the Configuration
Run the display mpls l2vpn track route command to check information about the association between the PW status and VPNv6 route status on an AGG.