Example for Configuring Load Balancing Among Tunnels to Which Remotely Leaked IPv6 VPN Routes Recurse
If there are multiple tunnels between PEs on the backbone network, configuring load balancing among tunnels can fully utilize network resources and enhance the reliability of VPN services on the backbone network.
Networking Requirements
If multiple tunnels, such as LDP LSPs and TE tunnels, exist between PE peers on the MPLS backbone network of a BGP/MPLS IPv6 VPN, load balancing among tunnels can be configured to distribute IPv6 VPN traffic to the tunnels and prevent network congestion.
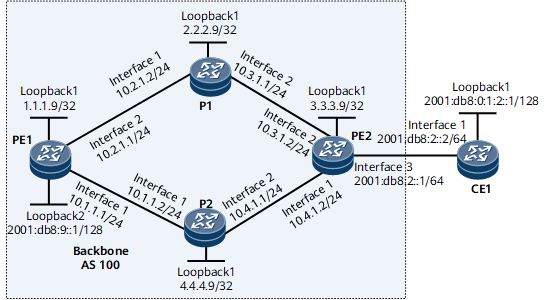
On the network shown in Figure 1, two links exist between PE1 and PE2 in the basic BGP/MPLS IPv6 VPN networking: an LDP LSP (PE1-P1-PE2) and a TE tunnel (PE1-P2-PE2). All IPv6 VPN traffic is forwarded over the LSP according to the default tunnel policy, which may cause the link of PE1 <-> P1 <-> PE2 to be busy and the link of PE1 <-> P2 <-> PE2 to be idle.
To address this issue, configure load balancing among tunnels on the MPLS backbone network to distribute IPv6 VPN traffic evenly to the two tunnels.
Configuration Notes
When configuring load balancing among tunnels to which remotely leaked IPv6 VPN routes recurse, ensure that the tunnels existing in the system can meet the requirements of the configured tunnel policy.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure OSPF on the MPLS backbone network to ensure IP connectivity on the backbone network.
Configure MPLS, MPLS LDP, and MPLS TE both globally and per interface on required devices of the MPLS backbone network and establish an LDP LSP and an MPLS TE tunnel between PEs.
Configure an IPv6-address-family-supporting VPN instance on each PE and bind the interface that connects a PE to a CE to the VPN instance on that PE.
Create a tunnel policy on PE1 to distribute traffic to the LDP LSP and TE tunnel between PE1 and PE2.
Apply the tunnel policy to the VPN instance IPv6 address family on PE1.
Procedure
- Configure a basic BGP/MPLS IPv6 VPN.
For configuration details, see Example for Configuring a Basic BGP/MPLS IPv6 VPN.
Configure OSPF on the MPLS backbone network so that the PEs can learn the routes to each other's loopback interface.
Configure MPLS and MPLS LDP both globally and per interface on PE1, P1, and PE2 to set up an LDP LSP along the PEs.
Establish a VPNv6 peer relationship between PEs.
Configure a VPN instance that supports the IPv6 address family on each PE and bind the interface that connects a PE to a CE to the VPN instance on that PE.
Enable BGP between the PEs and CE and import the routes to the loopback interface into BGP on the CE.
- Enable MPLS TE on PE1, P2, and PE2 and establish TE tunnels between PEs. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After completing the configurations, run the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance command on PE1. The command output shows that PE1 has learned the route to the loopback interface on the CE.
<PE1> display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 Routing Table : vpn1 Destinations : 4 Routes : 4 Destination : 2001:db8:0:1:2::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::FFFF:3.3.3.9 Preference : 255 Cost : 0 Protocol : BGP RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x800011 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : RD Destination : 2001:db8:9:: PrefixLength : 28 NextHop : 2001:db8:9::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : LoopBack2 Flags : D Destination : 2001:db8:9::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : LoopBack2 Flags : D Destination : FE80:: PrefixLength : 10 NextHop : :: Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : NULL0 Flags : D <PE1> display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 2001:db8:0:1:2::1 verbose Routing Table : vpn1 Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:db8:0:1:2::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::FFFF:3.3.3.9 Preference : 255 Neighbour : ::3.3.3.9 ProcessID : 0 Label : 1027 Protocol : IBGP State : Active Adv Relied Cost : 0 Entry ID : 21 EntryFlags : 0x80024904 Reference Cnt: 2 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0x24 Age : 895sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0000000001004c4ba2 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : RDThe command output shows that PE1 recurses the route to 2001:db8:0:1:2::1/128 to only the LSP since no tunnel policy is applied to the VPN instance IPv6 address family, and the outbound interface is GE 0/1/8.
- Apply the tunnel policy to the VPN instance IPv6 address family on PE1.
Configure a tunnel policy in select-sequence mode to make tunnels be selected in the order of TE tunnels and LSPs and to set the number of tunnels participating in load balancing to 2.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] tunnel-policy te-lsp-l2 [*PE1-tunnel-policy-te-lsp-l2] tunnel select-seq cr-lsp lsp load-balance-number 2 [*PE1-tunnel-policy-te-lsp-l2] quit
# Apply the tunnel policy to the VPN instance IPv6 address family.
[*PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv6-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv6] tnl-policy te-lsp-l2 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv6] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configurations, run the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance verbose command on PE1. The command output shows that the route to the loopback interface on the CE recurses to two tunnels.
<PE1> display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 2001:db8:0:1:2::1 verbose Routing Table : vpn1 Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:db8:0:1:2::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::FFFF:3.3.3.9 Preference : 255 Neighbour : :: ProcessID : 0 Label : 1027 Protocol : BGP State : Active Adv Relied Cost : 0 Entry ID : 21 EntryFlags : 0x80024904 Reference Cnt: 2 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0x24 Age : 895sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x000000000300000001 Interface : Tunnel1 Flags : RD RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0000000001004c4ba2 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : RDLoad balancing between tunnels to which remote cross routes recurse is successfully deployed on the IPv6 VPN.
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance tnl-policy te-lsp-l2 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls mpls te mpls te cspf mpls rsvp-te # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # interface LoopBack2 ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:9::1 128 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.9 mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te reserved-for-binding # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # tunnel-policy te-lsp-l2 tunnel select-seq cr-lsp lsp load-balance-number 2 # return
P1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
P2 configuration file
# sysname P2 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 # mpls mpls te mpls te cspf mpls rsvp-te # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls mpls te mpls te cspf mpls rsvp-te # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1 64 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 2001:db8:2::2 as-number 65410 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2 64 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:0:1:2::1/128 # bgp 65410 router-id 10.10.10.10 peer 2001:db8:2::1 as-number 100 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization network 2001:db8:0:1:2::1 128 peer 2001:db8:2::1 enable # return