Example for Configuring the Controller to Run NETCONF to Deliver Configurations to Create an SR-MPLS TE Tunnel
This section provides an example for configuring the controller to run NETCONF to deliver configurations to create an SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
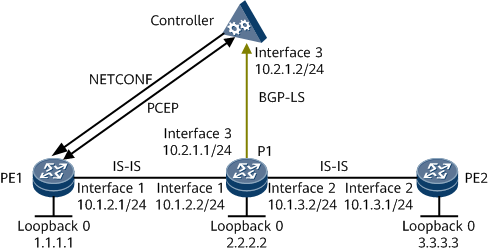
Networking Requirements
- IS-IS assigns labels to each neighbor and collects network topology information. P1 runs BGP-LS to collect topology information and reports the information to the controller.
- The controller uses the information to calculate a path and runs PCEP to deliver path information to ingress PE1.
- The controller sends the tunnel configuration information to the ingress node PE1 through NETCONF.
- The ingress node PE1 uses the delivered tunnel configurations and label stacks to establish an SR-MPLS TE tunnel. PE1 delegates the tunnel to the controller through PCE.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address and its mask to every interface and configure a loopback interface address as an MPLS LSR-ID on every node.
Configure LSR IDs and enable MPLS TE globally and on interfaces on each LSR.
Enable SR globally on each node.
Configure a label allocation mode and a topology information collection mode. In this example, the forwarders assign labels.
Configure the PCC and SR on each forwarder.
Configure the PCE server on the controller.
Procedure
- Assign an IP address and a mask to each interface.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface loopback 0 [*PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-LoopBack0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.2.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~P1] interface loopback 0 [*P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 32 [*P1-LoopBack0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.2.2 24 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.3.2 24 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip address 10.2.1.1 24 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface loopback 0 [*PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [*PE2-LoopBack0] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.3.1 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure IS-IS to advertise the route to each network segment to which each interface is connected and to advertise the host route to each loopback address that is used as an LSR ID.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface loopback 0 [*PE1-LoopBack0] isis enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] isis 1 [*P1-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 [*P1-isis-1] quit [*P1] interface loopback 0 [*P1-LoopBack0] isis enable 1 [*P1-LoopBack0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] isis enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface loopback 0 [*PE2-LoopBack0] isis enable 1 [*PE2-LoopBack0] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure PCE on the forwarders and controller. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic MPLS functions and enable MPLS TE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] mpls te [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
The configurations on P1 and PE2 are the same as the configuration on PE1. The configuration details are not provided.
- Enable SR globally on each node.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing [*PE1-segment-routing] quit [*PE1] commit
The configurations on P1 and PE2 are the same as the configuration on PE1. The configuration details are not provided.
- Configure a label allocation mode and a topology information collection mode. In this example, the forwarders assign labels.
Enable IS-IS SR-MPLS TE.
[~PE1] isis 1 [~PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] traffic-eng level-2 [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*PE1-isis-1] bgp-ls enable level-2 [*PE1-isis-1] commit [~PE1-isis-1] quit
The configurations on P1 and PE2 are the same as the configuration on PE1. The configuration details are not provided.
Configure the BGP-LS route advertisement capability on P1.
# Enable BGP-LS on P1 and establish a BGP-LS peer relationship with the controller.
[~P1] bgp 100 [*P1-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 [*P1-bgp] link-state-family unicast [*P1-bgp-af-ls] peer 10.2.1.2 enable [*P1-bgp-af-ls] commit [~P1-bgp-af-ls] quit [~P1-bgp] quit
# Enable BGP-LS on the controller and establish a BGP-LS peer relationship with P1.
[~Controller] bgp 100 [*Controller-bgp] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 100 [*Controller-bgp] link-state-family unicast [*Controller-bgp-af-ls] peer 10.2.1.1 enable [*Controller-bgp-af-ls] commit [~Controller-bgp-af-ls] quit [~Controller-bgp] quit
- The controller sends the tunnel configuration information to PE1 through NETCONF.
The detailed tunnel configuration delivered by the controller through NETCONF is as follows:
[~PE1] interface tunnel1 [*PE1-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 0 [*PE1-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*PE1-Tunnel1] destination 3.3.3.3 [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te tunnel-id 1 [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te signal-protocol segment-routing [*PE1-Tunnel1] mpls te pce delegate [*PE1-Tunnel1] quit [*PE1] commit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display mpls te tunnel command on PE1 to view SR-MPLS TE tunnel information.
[~PE1] display mpls te tunnel * means the LSP is detour LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Ingress LsrId Destination LSPID In/OutLabel R Tunnel-name ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.1.1.1 3.3.3.3 21 -/330000 I Tunnel1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- R: Role, I: Ingress, T: Transit, E: Egress
Run the display mpls te tunnel path command on PE1 to view path information on the SR-MPLS TE tunnel.
[~PE1] display mpls te tunnel path Tunnel Interface Name : Tunnel1 Lsp ID : 1.1.1.1 :1 :21 Hop Information Hop 0 Label 330002 NAI 10.1.2.2 Hop 1 Label 330002 NAI 10.1.3.1
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls mpls te # pce-client capability segment-routing connect-server 10.2.1.2 # segment-routing # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide bgp-ls enable level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 traffic-eng level-2 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack0 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol segment-routing mpls te tunnel-id 1 mpls te pce delegate # returnP1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls mpls te # segment-routing # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide bgp-ls enable level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 traffic-eng level-2 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.2.1.2 enable # link-state-family unicast peer 10.2.1.2 enable # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls mpls te # segment-routing # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide bgp-ls enable level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 traffic-eng level-2 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # returnController configuration file
# sysname Controller # pce-server source-address 10.2.1.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 100 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.2.1.1 enable # link-state-family unicast peer 10.2.1.1 enable # return