Example for Configuring Routing Loop Detection for Routes Imported from OSPF to IS-IS
This section provides an example for configuring routing loop detection for routes imported from OSPF to IS-IS.
Networking Requirements
On the live network, IS-IS routes can be imported to an OSPF process for redistribution. In such a scenario, routing policies are usually configured on multiple devices to prevent routing loops. If routing policies are incorrectly configured on the devices that import routes, routing loops may occur. To prevent this problem, configure routing loop detection for the routes imported to IS-IS.
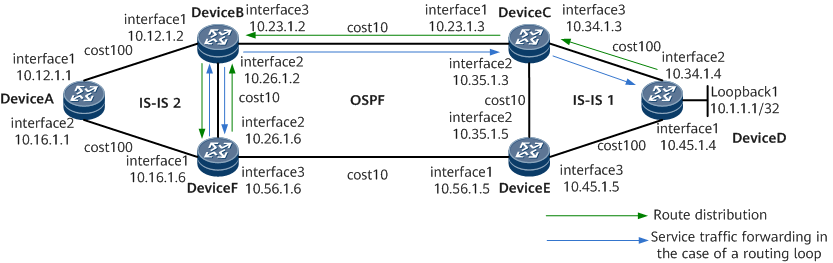
On the network shown in Example for Configuring Routing Loop Detection for Routes Imported from OSPF to IS-IS, IS-IS process 2 is configured on DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceF, an OSPF process is configured on DeviceB, DeviceC, DeviceE, and DeviceF, and IS-IS process 1 is configured on DeviceC, DeviceD, and DeviceE. DeviceC is configured to import routes from IS-IS process 1 to the OSPF process, DeviceB is configured to import routes from the OSPF process to IS-IS process 2, and DeviceF is configured to import routes from IS-IS process 2 to the OSPF process.

In this example, interface1, interface2, and interface3 represent GE0/1/0, GE0/1/8, and GE0/1/16, respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Disable routing loop detection, which is enabled by default.
Configure IP addresses for interfaces on each device to implement area connectivity.
Enable IS-IS and OSPF, and configure basic IS-IS and OSPF functions.
- Configure route import to construct a routing loop.
View routing entries to check whether a routing loop occurs.
- Enable routing loop detection and view routing entries to check whether the routing loop is eliminated.
Procedure
- Disable routing loop detection (enabled by default) on each device.
# Disable routing loop detection. DeviceA is used as an example.
<DeviceA> system-view [~DeviceA] route loop-detect isis disable [*DeviceA] route loop-detect ospf disable [*DeviceA] commit
The configurations of other devices are similar to those of DeviceA. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an IP address for each interface.
DeviceA, DeviceB, DeviceC, and DeviceD are used as examples.
# Configure DeviceA.
<DeviceA> system-view [~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.12.1.1 24 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.16.1.1 24 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure DeviceB.
<DeviceB> system-view [~DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.12.1.2 24 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.26.1.2 24 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip address 10.23.1.2 24 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceB] commit
# Configure DeviceC.
<DeviceC> system-view [~DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.23.1.3 24 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.35.1.3 24 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip address 10.34.1.3 24 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure DeviceD. The route 10.1.1.1/32 on the loopback interface of DeviceD is used as the locally originated route.
<DeviceD> system-view [~DeviceD] interface loopBack 1 [*DeviceD-LoopBack1] ip address 10.1.1.1 32 [*DeviceD-LoopBack1] quit [*DeviceD-LoopBack1] commit
The configurations of other devices are similar to those of the preceding devices. For details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable IS-IS and OSPF, and configure basic IS-IS and OSPF functions and a link cost to implement intra-area interworking.
# Configure IS-IS process 2 on DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceF. DeviceA is used as an example.
[~DeviceA] isis 2 [*DeviceA-isis-2] cost-style wide [*DeviceA-isis-2] network-entity 10.1111.0000.0001.00 [*DeviceA-isis-2] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 2 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis circuit-type p2p [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis cost 10 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 2 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis circuit-type p2p [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis cost 10 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceA] commit
The configurations of DeviceB and DeviceF are similar to those of DeviceA. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure IS-IS process 1 on DeviceC, DeviceD, and DeviceE. DeviceD is used as an example.
[~DeviceD] isis 1 [*DeviceD-isis-1] cost-style wide [*DeviceD-isis-1] network-entity 10.4444.0000.0001.00 [*DeviceD-isis-1] quit [*DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis circuit-type p2p [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis cost 10 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis circuit-type p2p [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis cost 10 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceD] commit
The configurations of DeviceC and DeviceE are similar to those of DeviceD. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure OSPF on DeviceB, DeviceC, DeviceE, and DeviceF. DeviceB is used as an example.
[~DeviceB] ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.23.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.26.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceB] commit
The configurations of DeviceC, DeviceD, and DeviceE are similar to those of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure route import.
# Configure DeviceC to import routes from IS-IS process 1 to the OSPF process.
[~DeviceC] ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-ospf-1] import-route isis 1 cost 100 type 2 [*DeviceC-ospf-1] commit
# Configure DeviceB to import routes from the OSPF process to IS-IS process 2.
[~DeviceB] isis 2 [*DeviceB-isis-2] import-route ospf 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-1] commit
# Configure DeviceF to import routes from IS-IS process 2 to the OSPF process.
[~DeviceF] ospf 1 router-id 6.6.6.6 [*DeviceF-ospf-1] import-route isis 2 cost 10 type 2 [*DeviceF-ospf-1] commit
- View the routing tables on DeviceB, DeviceE, and DeviceF to check whether a routing loop occurs.
# Check OSPF neighbor information on DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] display ospf peer (M) Indicates MADJ neighbor OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 2.2.2.2 Neighbors Area 0.0.0.0 interface 10.23.1.2 (GigabitEthernet0/1/16)'s neighbors Router ID: 3.3.3.3 Address: 10.23.1.3 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Master Priority: 1 DR: 10.23.1.3 BDR: 10.23.1.2 MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 3 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 28h43m46s Neighbor Up Time : 2021-08-23 09:20:09 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ] Area 0.0.0.0 interface 10.26.1.2 (GigabitEthernet0/1/8)'s neighbors Router ID: 6.6.6.6 Address: 10.26.1.6 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Master Priority: 1 DR: None BDR: None MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 4 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 28h43m46s Neighbor Up Time : 2021-08-23 09:20:09 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ]
# Check IS-IS neighbor information on DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(2) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6666.0000.0001 GE0/1/16 0000000011 Up 29s L1L2 -- 1111.0000.0001 GE0/1/8 0000000025 Up 27s L1L2 -- Total Peer(s): 2
The preceding command outputs show that DeviceB has established connections with DeviceA, DeviceC, and DeviceF.
# Check the routing table on DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] display ip routing 10.1.1.1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 1 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.1/24 O_ASE 150 1 D 10.26.1.6 GigabitEthernet0/1/16
The preceding command output shows that the next hop of the route displayed on DeviceB is DeviceF.
# Check OSPF neighbor information on DeviceF.
[~DeviceF] display ospf peer (M) Indicates MADJ neighbor OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 6.6.6.6 Neighbors Area 0.0.0.0 interface 10.56.1.6 (GigabitEthernet0/1/16)'s neighbors Router ID: 5.5.5.5 Address: 10.56.1.5 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Slave Priority: 1 DR: 10.56.1.6 BDR: 10.56.1.5 MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 4 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 28h52m49s Neighbor Up Time : 2021-08-23 09:20:11 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ] Area 0.0.0.0 interface 10.26.1.6 (GigabitEthernet0/1/8)'s neighbors Router ID: 2.2.2.2 Address: 10.26.1.2 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Slave Priority: 1 DR: None BDR: None MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 3 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 28h52m51s Neighbor Up Time : 2021-08-23 09:20:09 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ]
# Check IS-IS neighbor information on DeviceF.
[~DeviceF] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(2) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2222.0000.0001 GE0/1/8 0000000011 Up 28s L1L2 -- 1111.0000.0001 GE0/1/0 0000000011 Up 25s L1L2 -- Total Peer(s): 2
The preceding command outputs show that DeviceF has established connections with DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceE.
# Check the routing table on DeviceF.
[~DeviceF] display ip routing 10.1.1.1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 1 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.1/24 ISIS-L2 15 10 D 10.26.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8
The preceding command output shows that the next hop of the route displayed on DeviceF is DeviceB.
In this case, a routing loop is formed between DeviceB and DeviceF.
- Enable routing loop detection on each device.
# Configure DeviceA, which is used as an example.
[~DeviceA] undo route loop-detect isis disable [*DeviceA] undo route loop-detect ospf disable [*DeviceA] commit
The configurations of other devices are similar to those of DeviceA. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Check whether the routing loop is eliminated.
# Check the routing table on DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] display ip routing 10.1.1.1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 1 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.1/24 O_ASE 150 100 D 10.23.1.3 GigabitEthernet0/1/16
The preceding command output shows that the next hop of the route displayed on DeviceB is DeviceC.
# Check the routing table on DeviceF.
[~DeviceF] display ip routing 10.1.1.1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 1 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.1/24 ISIS-L2 15 10 D 10.26.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8
The preceding command output shows that the next hop of the route displayed on DeviceF is DeviceB and that DeviceB no longer prefers the route received from DeviceF. This means that the routing loop between DeviceB and DeviceF is eliminated.
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # isis 2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.1111.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.12.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 2 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 2 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # return
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # isis 2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.2222.0000.0001.00 import-route ospf 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.12.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 2 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.26.1.2 255.255.255.0 ospf network-type p2p ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 isis enable 2 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.23.1.2 255.255.255.0 ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 # ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # isis 1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.3333.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.23.1.3 255.255.255.0 ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.35.1.3 255.255.255.0 ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 isis enable 1 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.34.1.3 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 import-route isis 1 cost 100 type 2 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 # return
DeviceD configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # isis 1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.4444.0000.0001.00 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 isis cost 10 # returnDeviceE configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # isis 1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.5555.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.56.1.5 255.255.255.0 ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.35.1.5 255.255.255.0 ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 isis enable 1 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.45.1.5 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # ospf 1 router-id 5.5.5.5 import-route isis 1 cost 100 type 2 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 # return
DeviceF configuration file
# sysname DeviceF # isis 2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.6666.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.16.1.6 255.255.255.0 isis enable 2 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.26.1.6 255.255.255.0 ospf network-type p2p ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 isis enable 2 isis circuit-type p2p isis cost 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.56.1.6 255.255.255.0 ospf timer hello 1 ospf enable 1 area 0.0.0.0 # ospf 1 router-id 6.6.6.6 import-route isis 2 cost 10 type 2 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 # return