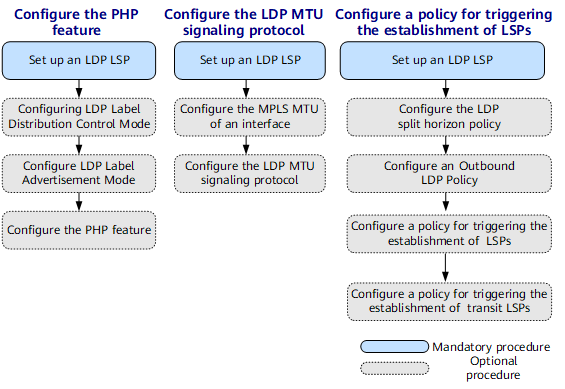
Configuring an LDP LSP
LDP is a label distribution protocol used to establish LSPs in an MPLS domain.
Usage Scenario
LDP can dynamically establish an LSP. An LDP LSP provided that LDP nodes do not need to be specified and traffic engineering (TE) does not need to be deployed on the MPLS network.
The maximum number of LSPs varies with the capacity and performance of a device. If too many LSPs are configured on a device, the device may operate unstably.
An LSP can be established only when eligible routes exist on LSRs and match the LSP setup policy. LDP can only use routes that match a specified policy to set up LSPs, which helps control the number of LSPs.
Policies for establishing ingress or egress LSPs are as follows:
LDP uses all IGP routes to establish LSPs
LDP uses host routes to establish LSPs.
LDP uses an IP prefix list to establish LSPs.
LDP does not establish LSPs.
To control the number of transit LSPs on a transit LSR, an IP prefix list can be used to filter routes, and only the routes matching the filtering policy can be used to establish transit LSPs.
To correctly select a path maximum transmission unit (MTU), an LSR must obtain the MTU of each link connected to it using LDP MTU signaling.
- Establishing an LDP LSP
- An LDP LSP can be automatically established only after an LDP session is established.
- (Optional) Configuring the PHP Feature
- The penultimate hop popping (PHP) function can be enabled after you configure a specific label on the egress before the egress assigns the label to the penultimate hop.
- (Optional) Configuring an LDP Label Advertisement Mode
- An LDP label advertisement mode can be configured to control LSP establishment.
- (Optional) Configuring a Global LDP Label Distribution Control Mode
- An LDP label distribution control mode can be globally configured to enable a local node to control the sequence of distributing labels to upstream nodes.
- (Optional) Configuring LDP to Automatically Trigger the Request in DoD Mode
- A remote LDP session must be configured before LDP is configured to automatically send requests in Downstream-on-Demand (DoD) mode
- (Optional) Configuring the MPLS MTU of an Interface
- An MPLS MTU can be configured on an interface to determine the maximum number of bytes in an MPLS packet that a device can forward without fragmenting the MPLS packet.
- (Optional) Configuring the LDP MTU Signaling Protocol
- LDP MTU signaling can be configured to allow Label Mapping message carrying MTU TLVs to be sent.
- (Optional) Configuring the LDP Split Horizon Policy
- An LDP split horizon policy can be configured to prevent an LSR from distributing labels to a specified downstream LDP peer.
- (Optional) Configuring the Inbound LDP Policy
- An inbound LDP policy can be configured to prevent the establishment of unwanted LSPs, efficiently using memory.
- (Optional) Configuring the Outbound LDP Policy
- An outbound LDP policy can be configured to prevent the establishment of unwanted LSPs, efficiently using memory.
- (Optional) Configuring a Policy for Triggering LSP Establishment
- A policy can be configured to enable LDP to use eligible routes to establish LSPs.
- (Optional) Configuring a Policy for Triggering the Establishment of Transit LSPs
- A policy for triggering the establishment of transit LSPs can be configured to enable LDP to use routes that meet the specified policy to establish transit LSPs.
- (Optional) Disabling LDP LSP Flapping Suppression
- LDP LSP flapping suppression helps effectively prevent label flapping. This function can be disabled.
- (Optional) Disabling a Device from Forwarding Unknown TLVs
- A local device can be disabled from forwarding unknown TLVs to peers.
- Verifying the LDP LSP Configuration
- After configuring an LDP LSP, you can view information about LDP and the LSP.